Short-run atmospheric conditions existing at a given time and location
A) wind
B) climate
C) weather
D) tornado
4. Seasonal winds on ‘water-land’ boundaries:
A) trade winds
B) totnado
C) monsoons
D) sirocco
5. Thermal inversion occurs when _______ air becomes sandwiched between two layers of ______ air and acts like a lid on a valley.
A) warm, cold
B) cold, warm
C) dry, humid
D) humid, dry
Which of the following air pollutants combines with atmospheric water to produce acid rain?
A) sulphur oxides
B) carbon monoxide
C) carbon dioxide
D) ozone
7. All of the following materials belong to primary air pollutants EXCEPT
A) particulate matter -
B) sulfur dioxide -
C) ozone
D) carbon monoxide -
E) nitrogen oxides-
8. Rivers and lakes contain more fresh water than groundwater.
A) True
B) False
9. The largest reservoir of fresh water:
A) groundwater
B) rivers and lakes
C) ice and glaciers
D) wetlands
10. Natural resource, the main asset of Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan:
A) oil and gas
B) mineral resources
C) water resources
D) coal deposits
11. Algal blooms in lakes
A) lead to an increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen present
B) are the result of excessive use of fertilizers on adjoining crop lands
C) cover large portions of the surface of the lake
D) all of the following
12. The part of Almaty below Tole bi street is more polluted with lead than the upper area of the city adjacent to the mountains.
A) True B) False
13. Life span of an energy-saving fluorescent bulb is ___________ than that of a regular incandescent bulb.
A) 10 times longer.
B) 80% less.
C) 10 times shorter.
D) 80% more.
14. Idea of recycling the matter is a distinctive feature of
A) classical economics
B) neoclassical economics
C) ecological economics
D) none of the above
15. Internal costs are expenses borne by
A) those who are using a natural resource.
B) by someone other than the individual/company who uses a natural resource
C) by the owner of the land, on which a natural resource is located
D) none of the above
16. Resources in Neoclassical Economics are considered as:
A) Resources exist in fixed (finite) amounts.
B) Expanded idea of resources: labor, knowledge, and capital.
C) Renewable and non renewable resources.
D) None of the above
17. All the following are the ways to achieve Urban Sustainability EXCEPT for:
A) Maintain greenbelts in and around cities.
B) Encourage walking and low-speed vehicles.
C) Recycling wastes and water.
D) Unlimited city size, unlimited population growth
18. Incandescent bulbs consume _____________ electricity than fluorescents bulbs
A) 2 times more
B) 5 times more
C) 5 times less
D) 2 times less
E) the same amount
19. Electricity represents
A) renewable energy source
B) primary energy source
C) secondary energy source
D) none of the above
20. The world's largest wind power producer
A) USA
B) Denmark
C) Canada
D) Netherlands
E) None of the above
21. Power is defined as
A) capacity to do work
B) rate of flow of energy
C) force
D) none of the above
22. _________________ possesses the largest oil resources in the world.
A) Russia
B) Kuwait
C) Saudi Arabia
D) Iran
E) Iraq
23. Fuel efficiency of 12.5 km per 1 L gasoline is equivalent to
A) 8 L per 100 km
B) 10 km/L
C) 50 mpg
D) none of the above
24. Gamma radiation is
A) high frequency electromagnetic radiation
B) high energy electromagnetic radiation
C) low wavelength electromagnetic radiation
D) all of the above.
25. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of
A) power
B) energy
C) force
D) work
E) B and D
26. What is the name of the type of energy derived from hot springs and geysers?
A) tidal energy
B) wave energy
C) hydropower energy
D) geothermal energy
27. The country with the largest natural gas reserves is
A) Russia
B) Iran
C) USA
D) Saudi Arabia
E) Afganistan
28. The second largest Biome in Kazakhstan:
A) deserts
B) steppes
C) semi-deserts
D) forests
29. The largest gas deposit in Kazakhstan is
A) Tengis
B) Kashagan
C) Karachaganak
D) Kalamkas
30. Urbanization is:
A) development of communications in rural side
B) increasing in Kazakhstan’s economics
C) propaganda of healphy lifestyle
D) emigration of urban population to the rural area
B. Fill in the blanks (0.5 x 2 = 1 point):
1._fossil___ __fuels____ are organic substances, created from decomposed dead plants, animals and other organisms in earth’ crust during millions of years.
2. Major problems, associated with nuclear power plants are ______safety___________ and _________health______.
C. Answer the following questions (5 pts):
1 (3 pts). Define the following major type of ecological problems: GLOBAL CHANGES.
Justify your answer with proper examples.
If changes have world-wide repercussions, such as the release of carbon dioxide when tropical rain forest is burnt, or involve a major portion of a global resource, or if a series of local changes accumulate to have a impact, as in accelerated soil erosion, these are global changes.
2(2 pts). Name several types of WATER POLLUTION, indicate their harmful impact.
Surface Water Pollution
These are the natural water resources of the Earth. These are found on the exterior of the Earth's crust, oceans, rivers and lakes.
Groundwater Pollution
Considerable amount of Earth's water is found in soil or under rock structures called aquifers. People use aquifers to obtain drinking water and build wells to access it. In case this water becomes polluted, it is called groundwater pollution. This is caused by pesticide contamination from the soil and this can infect the drinking water and lead to huge problems.
Microbiological Pollution
This is a natural form of water pollution caused by microorganisms. Most of these microorganims thrive in water and fish, land animals and humans to become ill. Microorganims like bacteria, viruses and protozoa cause serious diseases like cholera. In poor countries, there are no facilities to treat polluted water and hence the health of people are affected.
Oxygen depletion Pollution
Microorganisms that thrive in water feed on biodegradable substances. When a lot of biodegradable material is mixed with water, the number of microorganims increase and utilize the available oxygen. This is called oxygen depletion. As oxygen levels in water are depleted, harmless aerobic microorganisms die and anaerobic microorganims prosper. Some anaerobic microorganisms are harmful to people, environment and animals and they produce toxins like ammonia and sulfides.
Nutrients
These are necessary for plant growth and development. Most of these are found in wastewater and fertilizers. These can cause excess weed and algae growth if there are large concentrations in water. Drinking water and clog filters can be contaminated. The algae use up the oxygen in the water and leave none for the surrounding marine life and this can damage other aquatic organisms.
Suspended Matter
As the molecules are very large to mix between the water molecules, some pollutants do not dissolve in water. This material is termed as particulate matter and can lead to water pollution. The suspended particles finally settle and form a thick silt at the bottom. The marine life on the floor of rivers and lakes are harmed. Biodegradable substances are suspended in water and raise the quantity of anaerobic microorganisms present. The toxic chemicals that are suspended in water are harmful to the development and survival of aquatic life.
Chemical
Agricultural and Industrial work has the use of many chemicals that can run-off into water and pollute it. Metals and solvents from industrial work pollute rivers and lakes. Aquatic life is endangered by these and made infertile. Pesticides are used to control weeds, insects and fungi. Run-off's of these pesticides poisons aquatic life. If birds, humans and other animals eat infected fish they may be poisoned. Petroleum is a different type of chemical pollutant that pollutes water by oil spills in case a ship ruptures. Oil spills have a localized effect on wildlife, but can spread for miles. This oil can cause the death of many fish and stick to the feathers of seabirds. This loses their ability to fly.
Pollution happens when silt and other suspended solids like soil, construction, washoff plowed fields enters river banks. Eutrophication occurs under natural conditions, lakes, rivers and other water bodies. This is an aging process that fills in the water body with sediment and organic matter. In case these sediments enter various water bodies, fish respiration is affected, plant productivity and water depth is decreased.
D. Solve the following problems (8 pts):
1 (5 pts). Popular Russian automobile Lada Kalina consumes 6.6 L per 100 km on highway, while similar class Japanese car Suzuki Swift reaches fuel efficiency rate equal to 13 km/L on the same type of road.
A) Which car is higher in fuel efficiency? Calculate the ratio of fuel efficiency rates of these two cars.
B) Which automobile has lower fuel consumption rate?
C) Find monthly emissions for these two cars, assuming that both cars have the same monthly mileage of 1200 km.
Car emission coefficient = 2.42 kg CO2/L.
2 (3 pts). Fluorescent bulb consumes 80% less electricity than regular incandescent bulb. Talgat decided to replace in his apartment five 100W regular bulbs with fluorescent bulbs producing the same light intensity. Assume that each bulb is working on average 6 hrs per day 330 days per year.
A) Calculate the amount of electricity in kWh saved per year after such replacement.
B) Estimate reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per year due to such replacement.
C) Calculate absolute (in tenge) and relative (in%) financial gain of Talgat’s family per year.
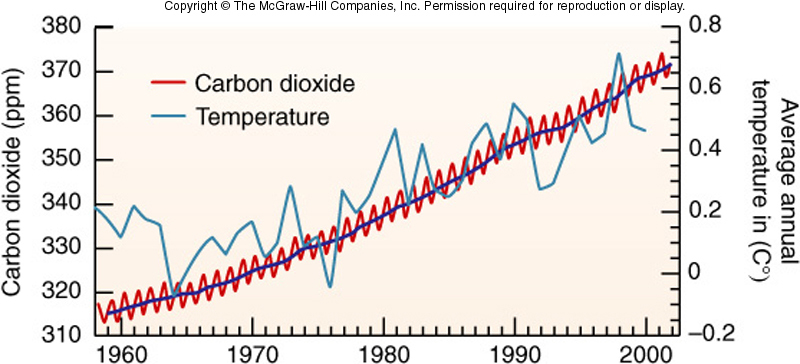
E. Graph analysis (8 pts).
The graph below represents evidence that supports global warming theory. Two curves: carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the atmosphere and temperature plotted versus time are given for the second part of 20th century.
a) From the graph find maximal and minimal carbon dioxide concentrations in years between 1970 and 2000. Calculate the relative rise in annual CO2 emissions (in %) during period of time 1970-2000 yrs.
b) Estimate average annual increment into CO2 concentration change for the time period of 1970 – 2000.
c) Based on the results received in (b) predict (calculate) CO2 concentration for 2010.
d) Compare the number received in c) with real CO2 concentration in the atmosphere, equal to 390 ppm.
 2018-01-08
2018-01-08 120
120






