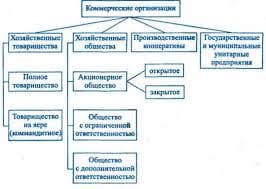
Rectifying diodes are used as rectifiers of a low frequency alternating current (50-100000 Hz) in commutation and control circuits. The energy of alternating current is transformed into the energy of direct current. The simplest rectifying circuit is shown in Fig. 3.7. This is a one-phase one half-cycle rectifier.

Fig.3.7. Circuit diagram of the rectifier
Let’s consider the operation of the simplest rectifier. Assume, that the secondary winding of a transformer is a source of a sinus changing voltage  . At first, we consider circuit operation without a capacitor. There is a positive voltage drop across a diode during the positive half-cycle. The flowing current
. At first, we consider circuit operation without a capacitor. There is a positive voltage drop across a diode during the positive half-cycle. The flowing current  forms the voltage
forms the voltage  drop across a load resistor
drop across a load resistor  .
.
During the negative half-cycle, there is no current flowing through the diode, therefore  . Thus the pulsated current flows through the diode and load resistor.
. Thus the pulsated current flows through the diode and load resistor.
In Fig 3.8c we can see the voltage drop across a diode  . The resistance of a load resistor is much higher than the resistance of a diode. So, when the forward current flows, the voltage drop across a load resistor is much larger than the voltage drop across a diode. During the negative half-cycle, the current doesn’t flow through the diode, and the secondary winding voltage applies completely to the diode. The direct component
. The resistance of a load resistor is much higher than the resistance of a diode. So, when the forward current flows, the voltage drop across a load resistor is much larger than the voltage drop across a diode. During the negative half-cycle, the current doesn’t flow through the diode, and the secondary winding voltage applies completely to the diode. The direct component  is a useful part of the pulsating voltage.
is a useful part of the pulsating voltage.  .
.

Fig.3.8. Voltage and current oscillograms of the rectifier circuit: a – input voltage, b – diode current and load voltage, c – diode voltage, d – load voltage with capacitor connected
The amplitude ratio of the direct and alternating components of rectified voltage is called pulsation factor:
 ,
,
where  – is the first harmonic of the Fourier series;
– is the first harmonic of the Fourier series;  - is direct component of rectified voltage.
- is direct component of rectified voltage.
For a one-phase one half-cycle rectifier Kpul =1.57. The smoothing filters are used to reduce Kpul.
Now we consider the operation of the rectifier with a resistance-capacitance load. Let’s connect the high-capacitance capacitor in parallel to the load resistor  . The capacitor will smooth pulsations well if
. The capacitor will smooth pulsations well if  .
.
The circuit operates in such a way. When the forward voltage is applied to a diode, the following current will charge the capacitor until  . When the current does not flow through a diode, the load resistor
. When the current does not flow through a diode, the load resistor  will discharge the capacitor, and the voltage drop across
will discharge the capacitor, and the voltage drop across  will come down slowly. Thus, the capacitor is charged through the low resistance of a diode and discharged through the load resistor. (Fig. 3.8 (d)) The capacitor raises the direct component of rectified voltage almost until
will come down slowly. Thus, the capacitor is charged through the low resistance of a diode and discharged through the load resistor. (Fig. 3.8 (d)) The capacitor raises the direct component of rectified voltage almost until  .
.
Such rectifiers are used in low-power circuits.
 2015-08-21
2015-08-21 391
391