Text 1
Financial management
Financial management consists of all the activities concerned with obtaining money and using it effectively. It involves careful planning and starts with determining the organization’s financial needs. The original investment by the owners is enough to get the business started. But income and expenses may vary from month to month and from year to year, leading to a need for temporary financing. Short-term financing is money that will be used in one year or one operating cycle, or less. Businesses typically need short-term financing due to cash flow, the movement of money into and out of an organization; speculative production, the time lag between the actual production of goods and when the goods are sold; or inventory issues. Credit transactions that may not be paid for in 30 or 60 days can create a need for short-term financing. Likewise, manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers make a significant investment in inventory, which can also create a need for short-term financing.
Long-term financing is money that will be used for longer than one year. It is frequently needed for business expansions and mergers, product development, marketing, and replacement of obsolete equipment.
Text 2
Leadership
Leadership is based on personal example, good management practices, and moral responsibility. Every supervisor in the company must set an example of company ideals and give personal attention and supervision to personnel below them in the chain of command. Leadership can be defined as the art of influencing people to progress towards the accomplishment of a specific goal. Leadership occurs when one person influences other people to work toward a definite goal.
You've heard the expression "leaders are born, not made" or "that person's a born leader". No one is "a born leader". Many people are natural leaders because of their strong, magnetic personality or because of their natural ability to learn rapidly. However, such people are the exception, not the rule. Because leaders aren't born, they must be trained. There are three elements that make an effective leader. They are moral principles, personal example, and administrative ability.
Moral principles include honesty, integrity, and loyalty. These principles of human conduct provide direction, solidity, and consistency to leadership. The key to leadership is the emphasis you place on personal moral responsibility. You show personal moral responsibility by being honest and loyal. Your shipmates see those traits as your moral character. And a strong moral character influences others in a positive manner.
Leading by personal example goes along with moral responsibility. Effective leaders have many leadership traits, such as know-how, sincerity, and courage. Which trait is the most important is a matter of opinion. However, if you show weakness in any trait a worker think is important, you lose that person's respect. Respect isn't automatically given to a leader because of authority. You have to earn respect and confidence.
Text 3
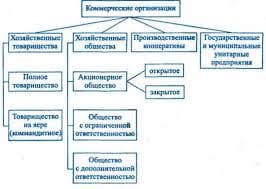
Business Structure
Business structures can vary as widely as the types of businesses that use them. When setting up a business, choosing the right structure can be critical to the success and life of the company.
Sole Proprietor: this is the most traditional form of business, where one simply goes into business in their own name or under a "doing business as" (DBA) trade name. It offers the least protection to the owner of the business but is the simplest to set up.
Partnership: this is another very common form of business ownership. It is created when two or more people or entities come together to do business, and can be the equivalent of a sole proprietorship in terms of its ease of set up and lack of legal protection. However, some jurisdictions have started to create variations on this form of ownership, such as the limited partnership, in an effort to provide some protection to business owners and/or to better define the relationships of the partners.
Corporations: this is a form of business ownership that creates a separate legal entity which is jointly owned by multiple investors. There are two primary forms of corporations: S and C. Each has its own unique advantages and disadvantages as related to raising capital and paying taxes.
Limited Liability Companies: these are a relatively new addition to the forms of business ownership. In simplest terms, it tends to combine some of the best features of partnerships and S Corps, such as ease of organization and pass through taxation.
Text 4
Human Resource Management
Human resource management is a part of every manager's responsibilities. These human resource responsibilities include placing the right person in the right job, and then orienting, training and compensating to improve his or her job performance. Human resource management is involved in both the formulation and the implementation of a company's strategies given the need for the firm to galvanize employees into a competitive advantage.
The policies and practices one needs to carry out the people or human resource aspects of a management position include recruiting, screening, training, rewarding and appraising.
Human Resource Management can be defined as management of activities undertaken to attract, develop, motivate, and maintain a high-performance workforce within organizations. The most important responsibilities of a Human Resource Manager are:
· Planning labor needs and recruiting candidates
· Orienting and training new employees
· Managing wages and salaries
· Providing incentives and benefits
· Communicating (interviewing, counselling, disciplining)
· Building employee commitment
Job analysis defines the task involved in a job, determines the relationship between different jobs, and ascertains the knowledge, skills and abilities necessary for an employee to perform job successfully. Job analysis produces information which is then used for developing job descriptions and job specifications. Job description is a statement that mentions what a job holder does and how and why does he do that. Job specification is a list minimum qualification that every employee must possess for successful performance of any job.
Text 5
SMART Business Goals
Whether you have a 50-employee company or an empire of one, your business success depends on your ability to set and achieve goals. Put your business on the fast-track by applying the principles of SMART goal setting.
S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for the 5 steps of specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based goals. It’s a simple tool used by businesses to go beyond the realm of fuzzy goal-setting into an actionable plan for results.
Specific – Is the goal specific enough for clarity?
Measurable – Is there a way to measure the goal? In other words, how do you know you achieved the goal?
Attainable – Is the goal truly attainable? Or is it such an outlandish goal that it looks good on paper but is nearly impossible to complete.
Realistic – Did you write the goal realistically? For example, did you address all the challenges of completing the goal and provide the necessary resources.
Timely – Is there a timeline associated with the goal to ensure a completion date?
So what does a smart goal look like? Based on the acronym, our example would state, “Obtain 2 new billion dollar corporate clients in the Boston property insurance market by the end of this fiscal year through networking and marketing activities.”
Once your business goals are SMART, break down each goal into a specific set of tasks and activities to accomplish your goals. It’s important to periodically review your goals and make adjustments if necessary. Goal setting for your small business is an essential tool for success. Remember in the end to be SMART.
3. Be ready to discuss the topic.
| 1.1 Forms of business organization |
| 1.2 Company structure |
| 1.3 Starting up business |
| 2.1 The manager’s role |
| 2.2 Top management role |
| 2.3 Communications |
| 2.4 Corporate culture |
| 3.1 Leadership |
| 3.2 Goal setting |
| 3.3 Business planning |
| 3.4 Decision making |
| 3.5 Motivation |
| 3.6 Performance appraisal |
| 4.1 Financial management |
| 4.2 Human resource management |
| 4.3 Production management |
| 4.4 Time management |
| 5.1 Management in multinationals |
| 5.2 Social responsibility |
| 5.3 Business ethics |
| 5.4 Managing across cultures |
| 6.1 Marketing principles |
| 6.2 Marketing mix |
| 6.3 Advertising |
| 7.1 Presentations |
| 7.2 Meetings |
| 7.3 Negotiating |
 2017-11-01
2017-11-01 784
784