What is GSM?
For other uses, see GSM (disambiguation).
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, originally Groupe Spécial Mobile) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation digital cellular networksused by mobile devices such as tablets, first deployed in Finland in December 1991. As of 2014, it has become the global standard for mobile communications – with over 90% market share, operating in over 219 countries and territories.]
2G networks developed as a replacement for first generation (1G) analog cellular networks, and the GSM standard originally described as a digital, circuit-switched network optimized for full duplex voice telephony. This expanded over time to include data communications, first by circuit-switched transport, then by packet data transport via GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) and EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution, or EGPRS).
Subsequently, the 3GPP developed third-generation (3G) UMTS standards, followed by fourth-generation (4G) LTE Advancedstandards, which do not form part of the ETSI GSM standard.
"GSM" is a trademark owned by the GSM Association. It may also refer to the (initially) most common voice codec used, Full Rate.
What is 3G?
3G (from the English. third generation — third generation), mobile technology 3 generations — a set of services that brings together high-speed mobile access with Internet services and radio technology, which creates a data channel. Currently, because of mass advertising campaigns, this term most often refers to the technology UMTS HSPA add-in
What is 4G?
4G is all the rage these days and at this point most people probably know that it’s faster than 3G, but there’s a whole lot more to it than that. So for a rundown of all the benefits, how to get 4G, exactly how fast it is and what the future holds read on, because we’ve got an easily digestible guide to everything you need to know.
What frequencies are used for 2G, 3G, 4G by Kazakhstan communication operators?
There are 3 network operators in the country from 2017:
§ Kcell
§ Beeline
§ Tele2 ( merging with Altel)
2G is up to EDGE on 900 MHz on all networks. 3G up to DC-HSPA+ on 2100 MHz on all networks. 4G/LTE started on Altel in 2013 on 1800 MHz and covers about 56% of the population in 2015. All of Kazakhstan’s cellular operators have launched 4G/LTE on 800 (band 20) and 1800 MHz (band 3) in every regional capital and expand services to most cities by the end by 2017.
Kcell and Beeline traditionally offer the best coverage and quality of service. In 2015 Tele2 and Altel (Kazakhtelecom) announced plans to put together their mobile operations in the country by creating a joint venture and merging their two networks in 2016/7. Altel shut down the last remaining CDMA network in 2015.
There are many small reseller offices in airports, train stations and shops, but their employees mostly don't speak English (except possibly in airports). You are required by law to present your ID at the point of purchase, but this can be enforced not so strictly.
Show the coverage areas in the RMS
Features of your smartphone:
| Brand Name | SAMSUNG |
| Model | SM-G357FZ |
| Operation System | Android 4.4 |
| SIM Card Quantity | TELE 2 |
| ROM | |
| CPU | |
| RAM | |
| 2G: | ü |
| 3G: | ü |
| 4G: | ü |
| Display Size | 480х800 |
| Battery Capacity(mAh) | 1900 (mAh) |
| Camera | the main- 5 Mp front- +1.3 Mp |
| Display Resolution | |
| Release Date | 2014, September |
TASK 3:
What is GPS?
GPS or Global Positioning System is a network of orbiting satellites that send precise details of their position in space back to earth. The signals are obtained by GPS receivers, such as navigation devices and are used to calculate the exact position, speed and time at the vehicles location.
GPS is well-known for its military uses and was first developed by the US to aid in its global intelligence efforts at the height of the Cold War.
Ever since the early 1980s, however, the GPS has been freely available to anyone with a GPS receiver. Airlines, shipping companies, trucking firms, and drivers everywhere use the GPS system to track vehicles, follow the best route to get them from A to B in the shortest possible time.
The very first GPS system was developed in the 1960s to allow ships in the US Navy to navigate the oceans more accurately. The first system had five satellites and allowed ships to check their location once every hour. Today, portable Navigation device devices can give drivers their precise location to within a few meters, which is accurate enough to navigate roadways. Military applications have much higher precision so that a location can be pinpointed within a few centimeters.
The US NAVSTAR Global Positioning System (GPS) is the only fully operational Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) currently providing positioning data with global coverage. The European Union is currently developing its own GPS known as the Galileo positioning system, which will be operational by 2013. China has a local system it may expand globally, while Russia is currently restoring its GLONASS system.
How does the GPS navigator work?
Using GPS navigation is becoming as commonplace as looking at a map. In-dash navigation systems are being installed in most new vehicles, portable GPS units are regularly used by hunters and hikers and GPS navigation can be enabled on most smartphones. But how does this technology work? How does that little receiver know where you are? It's actually a fairly simple process; however getting the infrastructure set up was quite the task. 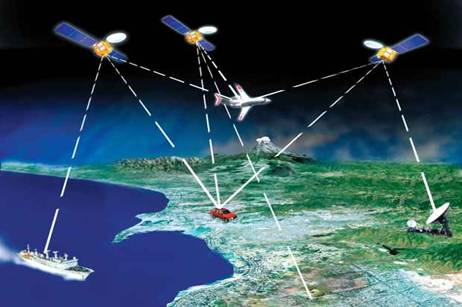
The basis of GPS are navigation satellites moving around the Earth in 6 circular orbital trajectories (for 4 satellites in each), at a height of 20180 km and the GPS Satellites revolve around the Earth in 12 hours, their weight in orbit is about 840 kg, dimensions – 1.52 m. wide and 5.33 meters in length, including solar panels, generating power 800 Watt. 24 satellites provide 100 % uptime of a GPS navigation system at any point of the globe. The maximum number of simultaneously working satellites in the system NAVSTAR is limited by the number 37. Currently in orbit is the satellite 32, 24 main and 8 backup in case of failures.
Briefly review popular GPS-navigators for smartphones:
a. Navitel
b. Yandex.Navigator
c. 2GIS
d. MAPS.ME
e. Google Maps
What do you use?
Show an example of use on your smartphone
 2018-02-13
2018-02-13 1619
1619