The Van’t Hoff law for dilute solutions permits calculation of the osmotic pressure as a function of solute concentration, that is,
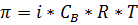
where π is the osmotic pressure (kPa)
CB is the concentration of solute ‘‘B’’ (mol/m3)
R is the universal gas constant (8.314510 N-m/g-mol K)
T is the temperature of solution (K)
To carry out the reverse osmosis process, one should put the pressure, P>π, in a system, that is
ΔP = P – π, kPa
Any additional pressure on the solution side, that is higher than the osmotic pressure will cause an increase in flux density from the solution side to the pure water side. The increase is proportional to the excess pressure, that is, net driving pressure (ΔP – π).
 2020-04-12
2020-04-12 128
128








