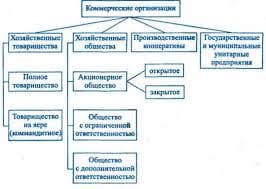
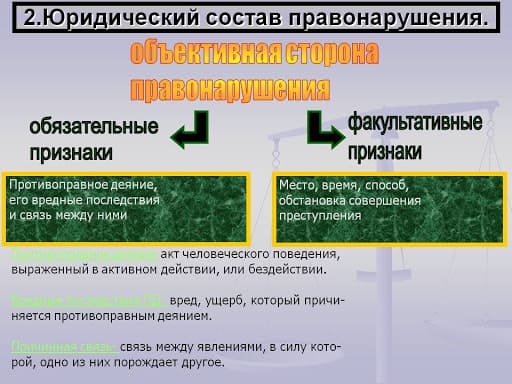
1. The tax, which is paid by the person on whom it is levied is known as the Direct tax while the tax, which is paid by the taxpayer indirectly is known as the Indirect tax. The direct tax is levied on person’s income and wealth whereas the indirect tax is levied on a person who consumes the goods and services.
2. The burden of the direct tax is transferable while that of indirect tax is non-transferable.
3. the incidence and impact of direct tax falls on the same person, but in the case of indirect tax, the incidence and impact falls on different [persons.
4. The evasion of tax is possible in case of a direct tax if the proper administration of the collection is not done, but in the case of indirect tax, the evasion of tax is not possible since the amount of tax is charged on the goods and services.
5. The direct tax is levied on Persons, i.e. Individual, HUF (Hindu Undivided Family), Company, Firm, etc. On the other hand, the indirect tax is levied on the consumer of goods and services.
6. The nature of a direct tax is progressive, but the nature of the indirect tax is regressive.
7. Direct tax helps in reducing the inflation, but the indirect tax sometimes helps in promoting the inflation.
8. Direct tax is collected when the income for the financial year is earned or the assets are valued at the date of valuation. As against this, the indirect taxes are collected, when the purchase or sale of goods or services are rendered.
9. Direct tax is imposed on and collected from the assessee. Unlike indirect tax is imposed on and collected from consumer but deposited to the exchequer by the dealer of goods or provider of services.
Similarities
• Payable to the government.
• Penalty for the non-payment.
• Interest on Delayed Payment.
• Improper administration can lead to tax avoidance or tax evasion.
Conclusion
Both the direct and indirect tax has its own merits and demerits. If we talk about the direct taxes they are equitable because they are charged on person, according to their paying ability. The direct tax is economical because its cost of collection is less but however, it doesn’t cover every section of the society.
On the other hand, if we talk about the indirect tax, they are easy to realize as they are included in the price of the product and services, and along with that, it has an excellent coverage of every section of the society. One of the best advantages of the indirect tax is, the rate of tax is high for harmful products as compared to the other goods which are necessary for life.
What is the difference between progressive and regressive tax rate?
A progressive tax is a type of tax that takes a larger percentage of income from taxpayers as their income rises. An example is the federal income tax, where there are six marginal tax brackets ranging from 10% (lowest-income taxpayers) to 39.6% (highest-income taxpayers). Most state income taxes have a similar progressive structure.
A regressive tax is the exact opposite. Higher-income taxpayers pay a smaller percentage of their income than lower-income taxpayers because the tax is not based on ability to pay. An example is state sales tax, where everyone pays the same tax rate regardless of their income.
When and why does government use progressive tax rate?
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. The term "progressive" refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the person's marginal tax rate. The term can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Progressive taxes are imposed in an attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability to pay, as such taxes shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay. The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, where the relative tax rate or burden decreases as an individual's ability to pay increases.[5]
The term is frequently applied in reference to personal income taxes, in which people with lower income pay a lower percentage of that income in tax than do those with higher income. It can also apply to adjustments of the tax base by using tax exemptions, tax credits, or selective taxation that creates progressive distribution effects. For example, a wealth or property tax,[8] a sales tax on luxury goods, or the exemption of sales taxes on basic necessities, may be described as having progressive effects as it increases the tax burden of higher income families and reduces it on lower income families.[9][10][11]
Progressive taxation is often suggested as a way to mitigate the societal ills associated with higher income inequality,[12] as the tax structure reduces inequality,[13] but economists disagree on the tax policy's economic and long-term effects.[14][15][16] Progressive taxation has also been positively associated with happiness, the subjective well-being of nations and citizen satisfaction with public goods, such as educationand transportation.
 2018-02-13
2018-02-13 565
565