Metabolism and energy - the main condition of life
It consists of two processes: the synthesis of substances - anabolism and decay-catabolism.
The body receives nutrients: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, they are broken down in the intestines before form transfer, absorbed into the blood, then two ways: either decay to simple substances with the release of energy, or the synthesis of complex substances for the construction of tissues (proteins, fats and carbohydrates, characteristic of the organism) with energy absorption.
Types of energy in the body.
The chemical energy of nutrients in the body goes into: chemical, electrical, mechanical and thermal energy.
The law of conservation of matter and energy (M. Lomonosov) is as follows: matter does not arise from nothing and does not disappear without a trace, but passes from one species to another.
This law operates in the human body, i.e. how many kilocalories have been ingested, so much can be spent, it is the basis of compiling food rations.
Five professional groups are singled out: people of mental labor, with light, medium, heavy and very heavy physical labor (from 2500kcal in the first group to 4500kcal in the fifth),
Also rations for patients, for the elderly, for children, athletes are compiled.
Exchange of proteins
Plastic role: are the building substrate for cell membranes; collagen and elastin in connective tissue; contractile muscle proteins: actin and myosin; proteins of blood plasma, hormones, enzymes. The body receives proteins of animal and vegetable origin, digestion into the digestive tract to amino acids and absorbed into the blood, then proteins are synthesized that are characteristic of the organism. The energy role of proteins: when 1 g of protein breaks down 4 kcal is released.
Protein metabolism is estimated by the amount of nitrogen entering the body and excreted from the body.
Nitrogen balance: received nitrogen = output nitrogen.
The wear coefficient is the smallest protein loss = 32 g per day (with fasting).
Regulation of protein metabolism
STH (somatotropic hormone of the pituitary gland) - stimulates protein synthesis, body growth.
Tнyroxin (thyroid gland) - stimulates the synthesis of protein, with a lack of fat and carbohydrates stimulates the breakdown of the protein.
Androgens (male sex hormones) - stimulate protein synthesis
Glucocorticoids (adrenal cortex) translate proteins into carbohydrates.
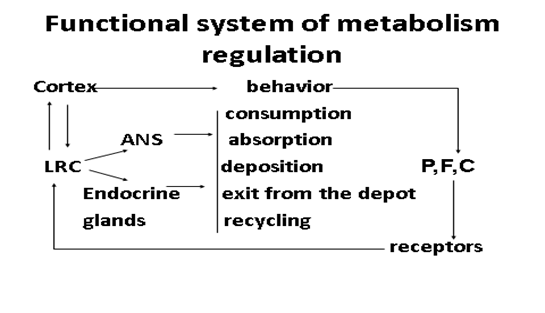
Nervous regulation - in the hypothalamus is the center of metabolism, which adapts it to the needs organism.
Exchange of carbohydrates
Plastic role: are the components of membranes, form the basic substance of connective tissue; glucose is contained in the blood plasma.
Energy function: oxidation of 1 g of glucose leads to the formation of 4 kcal. In the liver (as well as skeletal muscles and heart) contains glycogen (total 400 g), the decay of which produces glucose.
Fat exchange
Plastic role: lipids form adipose tissue (subcutaneous fat, body fat membranes); phospholipids - precursors of enzymes, hormones; Cholesterol is the precursor of steroid hormones.
Energy role: 1 g of fat during decay produces 9 kcal. In the body there is a depot of fat, but they are used only when there is a shortage of carbohydrates.
Regulation of fat metabolism
STH, thyroxine - stimulate the breakdown of fat.
Glucocorticoids - inhibit the oxidation of fats.
Insulin (a hormone of the pancreas) - transfers glucose to fat, stimulates the synthesis of fat from fatty acids.
Adrenaline stimulates the breakdown of fat.
Energy Exchange
Total energy exchange: (Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) + Thermic Effect of Activities(TEA) + Thermic Effect of Feeding (TEF)
(Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) (1600 kcal)
Thermic Effect of Feeding (TEF) 15% of BMR
1) thermoregulation
2) mental work - 3% of BMR
3) physical labor - 50 - 100% of BMR
4) emotional load - 15% of BMR
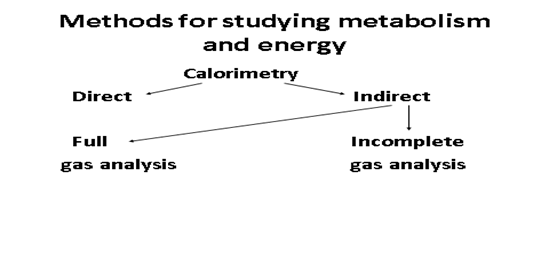
Incomplete gas analysis
1) the definition of Volume of absorbed O2
2) use the caloric equivalent for mixed nutrition (4.86 Kcal / L O2)
3) volume of absorbed O2 x caloric equivalent of O2
 2020-07-01
2020-07-01 256
256







