I. Read and memorize the following words and word combinations:
be little intimidating – немного пугающие
solder – припой
to pop in – заглянуть
insight – понимание сути
troubleshooting process – процесс поиска неисправности
tangible objects – материальные объекты
chassis – блок
to comprise – включать
circuitry – схема
II. Read and translate the text.
Some people get a little excited when they look inside a computer and see all the different electrical components and circuit boards. All the wires, connectors and data cables inside tend to be a little intimidating. Yet, all of today’s computer repairs, replacements, upgrades and installations are getting easier and easier.
A technician could spend hours to search for a specific chip or failed solder connection that’s causing a particular problem. Repairs aren’t done at the chip level anymore. Everything is very modular. It’s quicker, easier, and much more economical to have the technician pop in a whole new video card or motherboard.
It’s necessary to know some of the different components and what they do. It can give you an insight as to which particular module may need replacement, and aids in the troubleshooting process.
A personal computer is made up of multiple physical components of computer hardware, upon which can be installed an operating system and a multitude of software to perform the operator's desired functions.
The term “hardware” covers all those parts of a computer that are tangible objects. Circuits, displays, power supplies, cables, keyboards, printers and mice are all hardware.
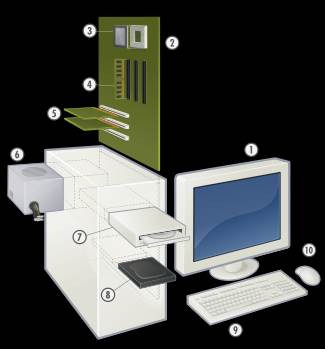
Though a PC comes in many different form factors, a typical personal computer consists of a case or chassis in a tower shape (desktop) and the following parts:
1. Monitor
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM
5. Expansion card
6. Power supply
7. CD-ROM drive
8. Hard disk
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
III. Give the Russian equivalents.
Computer case, connector, to install, wire, circuit board, connector, technician, upgrade, multitude, chassis, keyboard, replacement, troubleshooting.
IV.Give the English equivalents.
Корпус компьютера, соединитель (разъем), установить, монтажная плата, соединитель, техник, карта расширения, обновление, множество, блок, клавиатура, замена, провод (проводник).
V. Have a look at the picture and label the elements of this computer system.
VI. Translate the words of the same root. Define speech parts.
To connect – a connector – connection – connectible; to install – installation – an instalment; a place – to place – to replace – a replacement; a multiple – multiplication – to multiply – a multiplicator; to perform – performance – a performer.
VII. Complete the sentences according to the text.
1. All the wires, connectors ____ inside a computer sometimes tend to be a little intimidating. 2. A technician spent hours to search for a specific ____ or failed solder connection that’s causing a particular problem. 3. It’s quicker, easier, and much more economical to have____ in a whole new video card or motherboard. 4. The term ____covers all those parts of a computer that are tangible objects. 5. A personal computer is made up of multiple_____ of computer hardware.
VIII. Think of ways in which you can describe:
a) the term “hardware”
b) the PC modular system
c) computer’s hardware.
Lesson 2. Processing
I. Before reading the text try to answer the following questions:
1. What is the main function of a computer’s processor?
2. What unit of frequency is used to measure processor speed?
II. Read the text.
The nerve centre of a PC is the processor, also called the CPU, or central processing unit. This is built into a single chip that executes program instructions and coordinates the activities that take place within the computer system. The chip itself is a small piece of silicon with a complex electrical circuit called an integrated circuit.
The processor consists of three main parts.
The control unit examines the instructions in the user’s program, interprets each instruction and causes the circuits and the rest of the components — monitor, disk drives, etc. — to execute the functions specified.
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) performs mathematical calculations (+, -, etc.) and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT).
The registers are high-speed units of memory used to store and control data. One of the registers (the program counter, or PC) keeps track of the next instruction to be performed in the main memory. The other (the instruction register, or IR) holds the instruction that is being executed.
The power and performance of a computer is partly determined by the speed of its processors. A system clock sends out signals at fixed intervals to measure and synchronize the flow of data. Clock speed is measured in gigahertz (GHz). For example, a CPU running at 4GHz (four thousand million hertz, or cycles, her second) will enable your PC to handle the most demanding applications.
III. Answer the questions.
1. What are the main parts of the CPU? 2. What does ALU stand for? What does it do? 3. What is the function of the system clock? 4. How much is one gigahertz?
IV. What do the words in bold type refer to?
1. This is built into a single chip.
2. ___ which executes program instructions and coordinates….
3. ___ that is being executed.
4. ___performance of a computer is partly determined by the speed of its processor.
V. Translate the following text in writing.
The central processing unit (CPU) is the main IC chip on your computer’s motherboard. They come in different shapes, sizes and packages. Older CPUs came in the DIP format, and some 286s and early 386s were QSOPs, but what you’ll see the most are the flat, square PGA or SPGA chips.
CPU is considered the “brain” of your computer. It controls and directs all the activities of the computer, transmitting, receiving and processing data constantly. But like the “brain” of any project or organization, it relies very heavily on its support group and advisors. There are a lot of factors involved that are related to the CPU and have an effect on the speed and performance of your machine. Some of these factors include:
a) Whether there’s a math coprocessor present and if it’s internal or external.
b) The clock speed of the system and of the CPU. The amount of internal cache and external cache available.
c) The bus architecture or supporting circuitry on the motherboard.
Notes
DPI – Dual Inline Package – корпус с двумя рядами контактов; QSOP – Quarter Size Outline Package – корпус шириной в ¼ дюйма; PGA – Pin Grid Array – корпус с матрицей игольчатых приводов; SPGA – Staggered Pin Grid Array – ступенчатая матрица приводов; clock speed – тактовая частота; cashe – «кэш», промежуточная память с большой производительностью
 2020-10-11
2020-10-11 296
296








