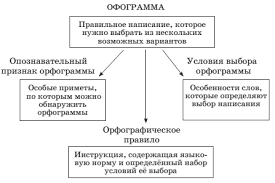
TEXT 1
In American higher educational institutions the individual courses that make up the degree program can be divided into the following types:
· Core courses: These provide the foundation of the degree program and are required of all students. Students take a variety of courses in mathematics, English, humanities, physical sciences, and social sciences. Some colleges require students to take many core courses, while other schools require only a few.
· Major courses: A major is the subject in which a student chooses to concentrate. Most students major in one subject; however, some colleges offer the option of pursuing a double major with a related subject. Your major courses represent one-quarter to one-half of the total number of courses required to complete a degree.
· Minor courses: A minor is a subject in which a student may choose to take the second greatest concentration of courses. The number of courses required for a minor tends to be half the number of major courses.
· Elective courses: These courses may be chosen from any department. They offer opportunities to explore other topics or subjects you may be interested in and help make up the total number of credits required to graduate.
American universities employ a system of continual assessment and assign grades for each course taken. Almost everything you do for a class will influence your final grade. Examinations and tests, essays or written assignments, laboratory reports, laboratory or studio work, class attendance, and class participation may all be used to determine your final grade. This means it is essential to keep up with the reading and course work and to attend classes on a regular basis.
TEXT 2
Bachelor's and Associate Degrees. The bachelor's degree typically takes four years to complete, though some students take slightly less time to finish, while others may take longer. The associate degree usually takes two years to complete. Associate degree programs are offered at two-year colleges known as junior or community colleges. Four-year colleges and universities offer bachelor's degree programs.
The U.S. Bachelor's Degree. You can usually choose from a wide variety of courses and create your own unique program of study. The degree is awarded after you complete a specified number of credits, which are usually completed in four years of full-time study. The first year is called the freshman year; the second is called sophomore; the third, junior; and the fourth, senior.
The academic year will be slightly different for each university or college but normally runs from early September to the end of May. It may be divided into two terms of 18 weeks called semesters. Alternatively, the university may have "quarters" or "trimesters," which are about 12 weeks in length. In addition, universities very often provide six- to eight-week summer terms. These are optional, and students attend if they wish to get through their degree faster, to decrease their course load during the regular terms, or to make up for courses not completed successfully during the regular academic year. There are at least two main holidays during the academic year: a two- to four-week break over Christmastime and a one-week "spring break" sometime between early March and mid-April.
TEXT 3
What is Distance Education?
Distance education is a type of formal learning in which the student and the instructor are not in the same place at the same time. The means of distance education include: mail and post offices; telephones and voicemail; one-way or interactive radio, television, satellite, audio, or video transmission; video cassette recorders (VCRs) or CD-ROMs; electronic mail (e-mail) and the Internet (e.g., Web-based learning).
For international students this means that they can study for a U.S. degree without leaving their home country, though they will almost certainly have to go to the United States for short periods of face-to-face contact and study on the campus.
Distance education can simulate the classroom experience through Internet chat-rooms, video-conferencing, and net-meetings in which the students can all join in to discuss topics and get immediate feedback from the instructor. Work for the course may require that a student be present at a given time for group or individual discussion.
Distance education is an increasingly popular way to study for everything from a short professional course to a doctoral degree in the United States. More than 90 percent of all accredited U.S. colleges and universities that have 10,000 or more students now offer distance education programs.
 2015-07-14
2015-07-14 750
750