A local area network (LAN) is a computer network covering a small geographic area, like a home, office, or group of buildings. Ex: a school (See Figure 11 below). The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to Wide Area Networks (WANs), include their much higher data transfer rates, smaller geographic range, and lack of a need for leased telecommunication lines. LANs can be small, linking as few as three computers, but often link hundreds of computers used by thousands of people. The development of standard networking protocols and media has resulted in worldwide propagation of LANs throughout business and educational organizations. The Figure 11 below shows a LAN consisting of six computers/work stations.
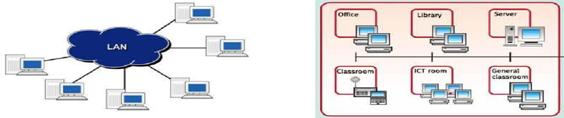
Figure 11- Local Area Network (LAN) Figure 12- LAN in a School
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Wide Area Network is defined as a group of computers and network devices connected across large physical areas such as states or countries. Computers connected to a Wide Area Network are often connected through the telephone system. They can also be connected through leased lines or satellites. One may define a WAN as a collection of several LANs as depicted in Figure 13 below.
The largest WAN in existence is the Internet. (You will learn about Internet in a coming section).
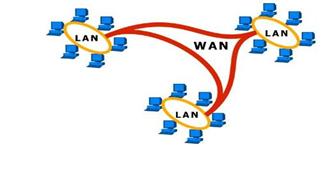
Figure 13- Wide Area Network
 2017-11-30
2017-11-30 1452
1452








