(CnO)KHh1e KOHCTPYKUHR C npqqacTBtM)
 K0HcTpYK11H¶, COCTomuaq H3 cyuteCTBwreJtbH01'O B 06ueM nane
K0HcTpYK11H¶, COCTomuaq H3 cyuteCTBwreJtbH01'O B 06ueM nane  MecrroHMCHH* B 06beKTBOM nane-7Ke H npHqac-rw, Ha3b1BaeTCq "Accusative with the Participle" ("CnONHoe aotiOJ']HeHue"), 3Ta KOHCTPYKI(HB rtepeBOA½Tcq Ha pvccKHìi.¶3biK qat_ne Bcero AOflOrIHHTe•1bHb1M 11PH.rraT0¼Hb1M flpcanoxeHne.M. OHa ynorpe6J1¶eycsy noc,.TJe rraKyx FJ]aro50B qyacrBeHHOFO BOCRPHHTH¶, KaK to feel, to hear, to see, to watch, to notice R I-A.
MecrroHMCHH* B 06beKTBOM nane-7Ke H npHqac-rw, Ha3b1BaeTCq "Accusative with the Participle" ("CnONHoe aotiOJ']HeHue"), 3Ta KOHCTPYKI(HB rtepeBOA½Tcq Ha pvccKHìi.¶3biK qat_ne Bcero AOflOrIHHTe•1bHb1M 11PH.rraT0¼Hb1M flpcanoxeHne.M. OHa ynorpe6J1¶eycsy noc,.TJe rraKyx FJ]aro50B qyacrBeHHOFO BOCRPHHTH¶, KaK to feel, to hear, to see, to watch, to notice R I-A.
E.g. watched him working at the text.
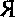 Ha6moaan, OH paõ0Tavr Ban Te-KCTOM.
Ha6moaan, OH paõ0Tavr Ban Te-KCTOM.
ll. K0HcrpYKt1H¶, COCTO%I.UUI CyueCTBHTe11bHOFO B 06me.M nane-
Ne JIM9HOFO MeCTOHMeHMS1 B nMe1fHTenbHOM 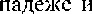 npuqac:rqq.
npuqac:rqq.
Ha361Bae•rcq "Nominative with the Participle" ("C.J]ŒKHOe 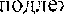
3ma 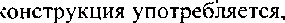 1-(0TAa c.Ka3veMOC Bblpa>f€eao FJral'OJIOM co 3uaqeHHe.M ouayuueHHfl. Bocllpptfll½h: to watch, to sec, to hear M T.A. E.g. He was watched working at the text.
1-(0TAa c.Ka3veMOC Bblpa>f€eao FJral'OJIOM co 3uaqeHHe.M ouayuueHHfl. Bocllpptfll½h: to watch, to sec, to hear M T.A. E.g. He was watched working at the text.
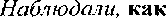 OH pa60raer Han TCKCTOM.
OH pa60raer Han TCKCTOM.
IIÍ•. KOHCTPYKMHH "CYl[œCTBHmeJ1bHOe + npwlacque 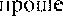
BPeNteHM" yr10Tpe6J]RTcq ß (þYHKu1tH CJIDKHOFO 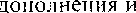 YKa_ñb1Baer Ha neñCTßHe, KOTopoe Bb1110]1HeHO MJIH Bb1110J11-\qercH He CatVIMM
YKa_ñb1Baer Ha neñCTßHe, KOTopoe Bb1110]1HeHO MJIH Bb1110J11-\qercH He CatVIMM 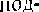
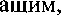 a KaKHM-TO ApyrHM JIHUO:M no.ue}Ka1uero H no ero
a KaKHM-TO ApyrHM JIHUO:M no.ue}Ka1uero H no ero 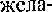 HMhO. 3•ra KOHCTPVKUM¶ ynorpe6nqeTcH noc.!xe r.naEOJ10B: to have, to get: to want, to wish COCTOHT "3
HMhO. 3•ra KOHCTPVKUM¶ ynorpe6nqeTcH noc.!xe r.naEOJ10B: to have, to get: to want, to wish COCTOHT "3 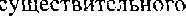 B 06111CM
B 06111CM 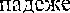
MeCTOhMe11L•iR naae)Ke H npw-vacT'1¶ rrpollœlll_nero apeMe-HEd.
E.g. He has the article translated.  EMY nepeBeJ]H c:raTb10.
EMY nepeBeJ]H c:raTb10.
Ex. 7. Translate the sentences with Participle Constructions:
l. The article being interesting and important, I used it ill  my report.
my report.
2. He sat watching TV, the newspaper forgotten on his knees.
3. He is going to have this job finished.
4. The door being opened. we heard the teacher speakin2 with a student.
5. Mike's uniform needs ironing, and Pete's shoes need polishing.
6. Mike had the TV set repaired some days ago.
7. The text being easy, the students could read and translate it easilv.
8. If read, the article must be discussed.
9. You must go to the hairdresser's and have your hair cut.
10. I heard him answering the question on the US Constitution.
1 1. The people want the public order being always maintained.
12. Freedom of speech and demonstration was reported be  ing violated.
ing violated.
13. The teacher felt him knowing that problem not quite
Ex. 8 Read the international words properly; give their equivalents in Russian:
C ongress; Senate: bills; resolutions; President; presidential; resident: programmes; to recommend; secretaries; advocates; interests; system; criminal; civil; constitution; nation.
Ex. 9. Give the corresponding verbs of the same root (KOPCHb) from the tòllowing words. Translate them:
 government: legislation; representative; election; head; interests; appaintment; trial; recommendation; composition; dependent; legislative.
government: legislation; representative; election; head; interests; appaintment; trial; recommendation; composition; dependent; legislative.
Ex. 10. Read the following words properly. Translate them. Use a dictionarv when necessary:
 an amendment; a government; a branch; executive; legislative; judicial; presidential; to be held; a resident; to cany out; to appoint; an ambassador, to be composed of; representatives; particular, to sign; to pass; 10 trv•, similar, entire; a governor.
an amendment; a government; a branch; executive; legislative; judicial; presidential; to be held; a resident; to cany out; to appoint; an ambassador, to be composed of; representatives; particular, to sign; to pass; 10 trv•, similar, entire; a governor.
 Read the fòllowing word combinations; translate them; trv to say them in English bv heart:
Read the fòllowing word combinations; translate them; trv to say them in English bv heart:
 by the Constitution of 1 787 and the amendments to it; the executive, legislative and judicial branches of power; the Congress of the United States; thc Senate and the House of Representatives; for a term of4 years: the number of yepresentatives from each state; to depend on the number Of people in each particular state; in order to be-come a law; to pass both the Houses: the executive power in the United States is vested in the President: the presidential election; to carry out the programmes of the Government; to appoint Federal Judges; ambassadors to Other countries; to be influential; Chief Justice of the USA; Associate Justices; to try cnminai and civil cases; the governor of the state.
by the Constitution of 1 787 and the amendments to it; the executive, legislative and judicial branches of power; the Congress of the United States; thc Senate and the House of Representatives; for a term of4 years: the number of yepresentatives from each state; to depend on the number Of people in each particular state; in order to be-come a law; to pass both the Houses: the executive power in the United States is vested in the President: the presidential election; to carry out the programmes of the Government; to appoint Federal Judges; ambassadors to Other countries; to be influential; Chief Justice of the USA; Associate Justices; to try cnminai and civil cases; the governor of the state.
Ex. 12. Read and translate the text:
US GOVERNMENT
By the Constitution of 1787 (and the amendments to it) the government of the USA is composed of three branches: the executive one. the
legislative one, and the judicial onc.
The highest executive power in the United States is vested in the President of the United States, who is elected for a term oc 4 vears by electors of each state. The Presidential election is held every four years in November. The President of the USA must be a native-born citizen, resident in the country for 14 years and at least 35 years old.
The President is to carry out the programmes of the Government, to recommend much of the legislation to the Congress. He is to appoint Federal Judges, ambassadors to other countries and heads of various government departments, called secretaries.
The legislative power belongs to the Congress of the United States consisting of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate is composed of two members from each state elected for a term of 6 years, one third being elected every two years. The number of representatives from each state to the House of Representatives depends on the number of people in each particular state.
In order to become a law all bills and resolutions must pass both the Houses and must be signed by the President.
An important role in the American legislation is played by so-called "lobbyists". They are often more influential than Congressmen themselves.
The Supreme Court is the highest judicial organ of the United States and the head of the judicial branch of power. The Supreme Court consists of the Chief Justice of the USA and a number of Associate Justices.
The United States is divided into I l judicial circuits, each one being served with a Federal Court of Appeals. There are about 90 district courts in different parts of the United States. The district courts are the lowest ones in the Federal court system. Most of the criminal and civil cases are tried by these courts.
Each state has a constitution similar to the Constitution of the entire nation and all the power in each state is divided into executive, legislative and judicial. The head of each state is the governor of the state.
Each state has each own system of courts similar to that of the Federal courts.
Ex. 13. Give as many word combinations as you can with the given words:
power (OCY"ÅeCTBJ1flTb, 6b1Tb 06"eqeHHb1M, ucnonHwreAbHaq,
3aKOHOAaœI¶bHas, c.YAe6Ha.H, 3KOHOMW1eC.KaH H T.lt.) to elect (Ha CPOK, npe_3HAeHTa, ceHaTopa, npencmaBHTeJ1*, nerjy-ra•ra H T.a.)  to appoint (rocYAapc•rBeHH0F0 cexperapl, Hoc..qa, npenccaa-renq cvna, flOMOLUHHKOB CYAbPf, apoKypopa, cyAbH) H T.A.) to try (yrOJlOBHOe ileJIO, rpa1•çnaHcKoe Aeno H T.A.)
to appoint (rocYAapc•rBeHH0F0 cexperapl, Hoc..qa, npenccaa-renq cvna, flOMOLUHHKOB CYAbPf, apoKypopa, cyAbH) H T.A.) to try (yrOJlOBHOe ileJIO, rpa1•çnaHcKoe Aeno H T.A.)
Ex. 14. Confirm or deny the statements using the following phrases:
Quite so... Right you are...
i quite agree with you here... or: I am afraid not...
 don't agree with you...
don't agree with you...
I am afraid you arc wrong...
Excuse me but...
On the contrary...
Not only...; not quite so...
 The government of the USA is composed of three branches.
The government of the USA is composed of three branches.
2. The executive power in the United States is vested in the Conuress.
3. The US President must be 40 years old.
4. The President of the USA carries out the programmes of the Government.
5. The President of the USA appoints secretaries of the Government.
6. The Congress of the United States heads the legislative power.
7. The Congress of the United States is the highest executive and the President is the highest legislative power in the USA.
8. In order to become a law all bills and resolutions must be signed by the President.
9. The Supreme Court is the head of the judicial branch of power in America.
10. The Supreme Court consists of the Chief Justice of the USA and  a number of the Associate Justices.
a number of the Associate Justices.
I l. There are I I judicial circuits in the United States.
12. Most of the criminal and civil cases are tried by district courts in the USA.
] 3. Each state in the USA has a constitution similar to the Constitu-
tion of the entire nation.
Ex. 15. Read the sentences completing them according to the text:
 By the Constitution of 1787 (and the amendments to it) the governmenl of the USA is composed of....
By the Constitution of 1787 (and the amendments to it) the governmenl of the USA is composed of....
2. The executive power in the USA is vested in the President or the USA who....
3. The President of the United States is to carry out... f to appomt..., to recommend....
4.  . must be a native-born citizen, resident in the countrv for..., and at least years old.
. must be a native-born citizen, resident in the countrv for..., and at least years old.
5. The legislative power in the USA belongs to... consisting or... 
6. The number of representatives from each statc to the House of Representatives depends on....
7. The Senate is composed of... elected for a term of 6 vears, onc third being elected every two vears.
8. In order to become a law all bills and resolutions Illust....
9. Lobbyists plav an important role in the American 

 The highest judicial organ in the United States is.., consisting of the Chief Justice of the USA and a number of Associate Justices.
The highest judicial organ in the United States is.., consisting of the Chief Justice of the USA and a number of Associate Justices.

l l. The lowest courts in the Federal court svstem arc... which try most of the criminal and civil cases.
12. The head of each state is....
Ex. 16. Change the sentences using Passive Voice:
Model: A Federal Court of Appeaìs serves each judicial circuit.
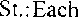 judicial circuit is served bv a Federal Court of Appeals.
judicial circuit is served bv a Federal Court of Appeals.  The executive, legislative and judicial branches of power compose the government of the USA.
The executive, legislative and judicial branches of power compose the government of the USA.
2. A Federal Court of Appeals serves each judicial circuit.
3. Two members from each state elected for a term of six vears compose the Senate.
4. So-called "Lobbyists" play an important role in the American legislation.
5. The district courts try most of the criminal and civil cases.
6. Electors from each state elect the President of the United States
for a term Of 4 vears.
7. The President recommends much of the legislation to the Congress.
8. The President appoints Federal Judges, ambassadors to other countries.
9. During the election campaign Reagan and his party spent much money in order to become the President of the USA.
Ex. 17. Read and translate the sentences paying attention to the pronoun "one":
 The government of the USA is composed of three branches: the executive one, the legislative one, and the judicial one.
The government of the USA is composed of three branches: the executive one, the legislative one, and the judicial one.
2. The district courts are the lowest ones in the Federal court systcm.
3. The constitutional system of each particular state is the one which is similar to that of the entire nation.
4. One can say that lobbvists in the American legislation are verv often more influential than the Congressmen.
5. Each voter in the US is in front of the choice between the candidates of two opposite parties: the republican one and the democratic one, whose political platforms are practically alike.
6. One should sav that politics in the USA as in many other countries is ''a commercial enterprise as any other one'.
7. In some countries the more money one can pay, the better lawyer one can have.
8. The USA is divided into 50 states; each one has its own constitution.
Ex. 18. Answer the following questions:
 What branches is the government of the USA composed of?
What branches is the government of the USA composed of?
2. Who does the highest executive power in the United States belong to?
3. What kind of person must the President of the USA be?
4. What are some of the functions of the President?
5. Who is the legislative power vested in?
6, How many chambers does the Congress consist of?
7. How many members are there in the Senate? in the House of Representatives?
8. What must all bills and resolutions pass in order to become a
9. What can you say about lobbvists?
10. What is the' head of the judicial branch of power in the United States?
l l. Who does the Supreme Court of the United States consist of?
12. Where are most of the cri:ninal and civil cases tried?
13. What kind of government does each state in the USA have?
Ex. 19. Read and translate the sentences with various forms of Participle:  The case being heard by the district people's court is of great interest for our students,
The case being heard by the district people's court is of great interest for our students,
2. Being divided into I l judicial circuits the USA has a Federal Court of Appeal in each circuit.
3. Having passed both the Houses the bill became a kaw.
4. Being divided into executive, legislative and judicial branches, all power in each statc is similar to that of the entirexlation.
5. Having tried this uneasy case the court passed a sentence.
6. Having arrived at the crime scene among the first, the investigator was able to question all persons present at the scene.
7. Being elected thr a term of 4 vears the President is to carry out the programme of the government.
8. Having been signed by the President the resolution came into force all over the country.
9. The number of paid lobbyists being three times greater than that of the members of the Congress, an important role in the American legislature is played by these lobbyists.
10. The political platform of the Republican and Democratic parties in the USA being alike, the Democrats and Republicans essentially conduct the similar policy.
l l. Each court of appeal in the circuit consists of between 3 and 15 judges depending upon the amount of work in the circuit, the judge with the largest service, who has reached his 70th birthday, being the chiefjudge.
Ex. 20. Speak about:
l, the executive branch of power in the U SA;
2. the Congress of the USA;
3. the judiciary in the USA.
i 62
Ex. 21. Read the following international words properly, translate them: political, practical. standards, basic, to tarrn, to interpret, historian, conservative. privileged class, position, preamble, pressure, satisfaction, guarantee, limit, individual, elemen tarv, control, oligarchy, to regulate, petition.
Ex. 22. Read and translate the words. Use a dictionary if necessary: language, re2ulations, custom, though, essentially, advantage. advantageous, wide-spread, significantly, bourgeois, to enumerate, to violate, enterprise, wealthy, at the expense of, unemployment. poverty, income. to profit.
Ex. 23. Read and translate the adverbs; give the corresponding adjectives they are formed of:
practically regularly, essentiallv collectively, properly, widely, significantly, relativelv, personally, carefully.
Ex. 24. Read, translate the word units, try to say them again by heart:
in American political language; the set of rules, laws, regulations and customs; Supreme Court decisions; to be aimed at preserving the advantageous position; to regard as an essentially conservative document; widespread dissatisfaction; guarantees of basic freedoms and individual rights; to consolidate •the gains of the Revolution; to be advantageous fòr the capitalist class; the elementary bourgeois-democratic freedoms; to violate the rights; freedom of enterprise: to expand personal freedoms; on the contrarv; in practice; freedom of the wealthy; at the expense of the working people: to face unemployment and povertv: to need a guaranteed income; a guaranteed health care.
Ex. 25. Read and translate the text:
US CONSTITUTION
The form of the U S government is based on the Constitution of 1 787, adopted after the War of Independence. A "constitution" in American political language means the set of rules, laws, regulations and customs which together provide the political norms or standards regulating the work of the government. The document known as the Constitution or the United States, though a basic document, is onlv a part of the bodv of
rules and customs which form the whole of the American Constitution. Supreme Court decisions, interpreting parts of the US Constitution, laws, regulations, customs are part of the basic law (the so-called live constitution). Most historians regard the US Constitution as an essentially con• servative document.
The US Constitution consists of the Preamble, seven articles and twenty six amendments, the first ten ofthcm called collectivelv the Bilk of Rights and adopted under the popular pressure in 1791. When thc Constitution was first proposed in 1787, there was widespread dissatisfaction because it didn't contain guarantees of certain basic freedorns and individual rights. The Constitution consolidated those gains of the revolution that were advantageous for the capitalist class. Significantly, nothing was said about the elementary bourgeois-democratic freedoms. In December, 1791, the Congress adopted ten amendments to the Constitution, known as the Bill of Rights. The Bill enurnerated what the government controlled by the oligarchy was not going to bc allowed to do. It was, of course, an important democratic gain for the people at that time. But nowadays some of these ten amendments are relatively unimportant.
 The Bill Of Rights is sometimes violated by the judicial and law enforcement practice.
The Bill Of Rights is sometimes violated by the judicial and law enforcement practice.
 Americans feel that of all the freedoms proclaimed in the Constitution only one freedom — freedom of enterprise is in fact guaranteed.
Americans feel that of all the freedoms proclaimed in the Constitution only one freedom — freedom of enterprise is in fact guaranteed.
If there is no freedom to work, no guaranteed labour, voU face unemptoyment and poverty. The main freedoms after all a man needs are a life of security, a guaranteed income and guaranteed health care, Notes:
 "live constitution" •'NHBaq KOHCTHTYUHA'
"live constitution" •'NHBaq KOHCTHTYUHA' 
2. what the government controlled by the oligarchy was not going to be allowed to do.. npaBHTenscTBY, KOTapoe fi0\1'Ÿpo-T'HpoBa  onurapxHeii, HC paapema_nocb AenaTb.
onurapxHeii, HC paapema_nocb AenaTb.
Ex. 26. Read and translate the sentences paving attention to Participle I.
 A "constitution" meaning in American political language the set of rules, laws, regulations and customs provides the practical norms and standards regulating the work of the èovernment.
A "constitution" meaning in American political language the set of rules, laws, regulations and customs provides the practical norms and standards regulating the work of the èovernment.
2. The US Constitution consisting of the preamble, seven articles and twenty six amendments was adopted in 1787.
 64
64
3. Being made up bv the privileged class the U S Constitution of  1787 didn't contain bourgeois-democratic freedoms.
1787 didn't contain bourgeois-democratic freedoms.
4. Having been proposed first in 1787 the Constitution faced widespread dissatisfaction because il did not contain guarantees of' certain basic freedoms and individual rights.
5. Having no guaranteed labor, guaranteed income and health care the working lilan is guaranteed inequality.
6. Being aimed at preserving the advantageous position of the ruling 'Sass the US Constitution of 1787 said nothing about the elementat-y democratic freedoms when it was first proposed.
Ex, 27. Say the tbllowing phrases using Participle [I:
Model: to base the government on the Constitution of 1787. 
St: the government based on the Constitution of 1 787.
to retyard the US Constitution as an essentiallv conservative document; to make this document for the ruling class; to aim the Constitution at preserving the advantageous position of the moneyed class; to call the first ten amendments as the Bilk of Rights; to propose the Constitution in 1 787; to control the government; to violate the Bill of Rights.
Ex. 28. Sav the sentences using the Passive Voice:
Model: In December 1791, the Congress adopted ten  amendments to the Constitution.
amendments to the Constitution.
St.: Ten amendments to the Constitution were adopted by the
Congress in December, 1 791.
 They said nothing about the elementarv bourgeois-democratic freedoms in the Constitution of 1787.
They said nothing about the elementarv bourgeois-democratic freedoms in the Constitution of 1787.
 The Constitution of 1787 bases the form of the US government.
The Constitution of 1787 bases the form of the US government.
3. The judicial and law-enforcement practice sometimes violate the Bill of Rights.
4. They proposed the Constitution first in 1787.
5. Most historians regard the US Constitution as an essentially conservative document.
6. The privileged class made the Constitution for themselves.
7. The ruling class aimed their constitution at preserving their interests.
Ex. 29. Give the English equivalents for the following:
CBOA 3aKOHOB, npaBHJ1, nocrraHOB-neHuV' H 06b1qaeB', CYMTaTb KOHCTH-
-ryumo CI_IJA. no cywecTBY, KOHCePBarMBHb1M AOKYMeHTOM', AOKYMeHT, npHH9Tb1V1 B 1787 rony H aononae11Hb1ä nonpaBKaMH', 11PHHHTb KOHCTHTYLU"O (gaKOH); LU½POKO pacrrpocTpaHeH110e '3']'-'MeHTapHble 6yp,KY'd3Ho-11eM0Kpa'tyqecKvte CB060Abr, Hapv1_11aTb O ce060aa 11PeA11PHHHMaTeJ1bCTBa; era.1KHBaThCH c 6egpa60Tuueä H 6eAH0CTbfo•, rapaHTHp0BaHHb1ii gapaõ0T0K; rapaHTupoBaHHaq oxpalia 
Ex. 30. Confirm or deny the statements using the following phrases:
It's right... 
Quite so....
 quite agree 'Nith it....
quite agree 'Nith it....
I don't agree with it....
Excuse me but... 
On the contrary....
I am afraid it is not quite so....
 The form of the US government is based on the Constitution of 1 787, adopted after tac War of Independence.
The form of the US government is based on the Constitution of 1 787, adopted after tac War of Independence.
2. The Bill of Rights is often violated in the USA,
3.  The US Constitution is regarded as a democratic document bv most historians.
The US Constitution is regarded as a democratic document bv most historians.
4. The privileged class made the Constitution tor the working peo  in 1787.
in 1787.
5. A litè of security, health care, income are guaranteed for all the people in America by the Constitution of the USA.
6. The US Constitution was adopted in 1787 and then was added bv amendments.
7. The US Constitution consists of the Preamble, seven articles and twenty-six amendnnents.
8. The people in America were not satisfied "'ith the Constitution Of 1787 because it didn't guarantee certain basic freedoms and individual rights.
Ex. 31. Read the sentences completing them according to the text:
 A "constitution" in American political language means which provide the political norms regulating the work of the govern-
A "constitution" in American political language means which provide the political norms regulating the work of the govern-
me-nt.
 Lobbyists in the USA are very often more than the Congress-
Lobbyists in the USA are very often more than the Congress-
men themselves.
3. The US Constitution consists of...
4 When the Constitution was first proposed in 1787, it didn't contain guarantees of' certain basic freedoms and individual rights, so there was....
5. The Bill of Rights is sometimes the judicial and lawenforcement practice.
6. You if there is no guaranteed labor.
7, A man needs the main freedoms that is guaranteed....
Ex. 32. Retell the text using the following key word combinations:
the set of rules, laws, regulations and customs; to be aimed at preserving the advantageous position; to contain guarantees of certain basic freedoms; ten amendments; to violate the Bill of Rights; guaranteed income, labour and health care; to face unemployment and poverty.
Ex. 33. Answer the questions:
l. What does a "constitution" in American political Ianzuage mean?
2. What is the US Constitution aimed at? Why?
3. What does the US Constitution consist of? 4. Why was there wide-spread dissatisfaction among the people when the Constitution was first proposed in 1787?
5. What did this dissatisfaction among the people lead to (result in)?
6. Was the adoption of the Bill of Rights an important democratic gain at that time?
7. What are the main freedoms a man needs?
Ex. 34. Give the explanation of the following in English:
a) US Constitution;
b) the Bill of Rights.
Part Il. Higher Bodies of State Power in the United Kingdom
Ex. l. Read properly the following names and terms:
Great Britain; the Prime Minister, number 10 Downing Street: the Houses of Pariiament; Westminster, Parliamentary govemment; the United Kingdom; government departments; ministers of the Crown; local authorities; statutory boards: the House of Lords; the House of Conunons.
Ex. 2. Read and translate the following words paying attention to the international root; economic; constitutional; apparatus; social; to concentrate; section; trusts; to control; industry, finance; police; monarchv. absolute; to limit; the Prime Minister, policy; committee; monopolists; parliamentary; politician; to direct; department; administration; operation; to nationalize; public services.
Ex. 3. Read the following word combinations after the speaker; then try to say them once again by heart:
to have a majority in the House of Commons; to take policy deci• sions; to make the changes in the size of Cabinet; to create new ministries; the power of the monopolists over the parliamentary government; by direct representation in Parliament', by direct influence over the Cabinet; by initiation, control and amendment of legislation; the bodies of the legislature; the bodies of the executive; the bodies of the judiciarv; the Queen in Parliament; ministers of the Crown; to be responsible for. local authorities; government departments; statutory boards; particular nationalized industries; hereditary power.
Ex. 4. Open the brackets using the verb '-to be" in a proper form:  The British state (to be) a capitalist state.
The British state (to be) a capitalist state.
2. The entire constitutional and state apparatus (to be) concentrated in the hands of the capitalist trusts.
3. The economic power in Great Britain (to be) in the hands of the tiny section of rich property owners.
4. Government departments in Great Britain (to be) responsible for administration at the national level.
S. The bodies of government in the United Kingdom (to be): a) those Of the legislature, b) those of the executive, and c) those Of the judiciary.
6. The British constitutiona] system (to be) an expression of the rule of capitalism.
7. The Cabinet and other ministers of the Crown (to be) responsible for directing national policy.
8. The highest legislative body in Great Britain (to be) the Queen in Parliament.
9. Great Britain (to be) a parliamentary monarchy. The Queen of Great Britain (to be) not absolute, but constitutional.
10. The powers of the Queen (to be) hereditary, not elective.
l l. The Prime Minister (to be) usually the leader of the party that has a majority in the House of Commons.
Ex. 5. Open thc brackets using the verbs in a proper lònn of the Present Indefinite Tense:
 The Prime Minister (to hold) Cabinet meetings at his or her house at number 10 Downing Street.
The Prime Minister (to hold) Cabinet meetings at his or her house at number 10 Downing Street.
 The Prime Minister usually (to take) policy decisions with the agreement of his Cabinet.
The Prime Minister usually (to take) policy decisions with the agreement of his Cabinet.
3. The rich property owners (10 control) the land, industry, finance, and trade in Britain.
4. Men of one and the same social class (to staff) the state apparatus, the British armed forces, the police and the judiciary.
5. The real power in Great Britain (to belong) to great trusts and monopolies.
6. Monopolists (to initiate and control) legislation in Britain.
7. The executive bodies in Great Britain (to consist) of
a) the Cabinet and other ministers of the Crown;
b)  government departments; c) local authorities and
government departments; c) local authorities and
d) statutory boards.
8. The entire constitutional and state apparatus (to remain) firmly in the hands of big monopolies.
9. The British constitutional system (to protect) the capitalist social order.
Ex. 6. Read the text "The Bodies of Government in the United
Kingdom" and answer the following questions on the text:  What kind of state is Great Britain?
What kind of state is Great Britain?
2  En what way do the monopolists achieve their power over the government in Britain?
En what way do the monopolists achieve their power over the government in Britain?
3. What are the branches of power in the United Kingdom?
4. What is the highest legislative body in the United Kingdom?
5. What do the executive bodies of Great Britain consist of?
 6. What kind of organ is the House of Lords?
6. What kind of organ is the House of Lords?
7. Who is responsible for directing national policy in Great Britain?
8. Who is responsible for the operation of public services in Great Britain?
9. What are local authorities responsible for?
10. What can you say about the Prime Minister of Great Britain?
 2017-11-30
2017-11-30 1044
1044