 Electronic Engineering 93
Electronic Engineering 93

 SPECIALIST READING A: Microcontroller Matter
SPECIALIST READING A: Microcontroller Matter

9. Scan the text and match the headings (a – h) with the paragraphs (1 – 8).
a) Watchdog;
b) BUS;
c) CPU;
d) General information;
e) Input-output unit;
f) Memory unit;
g) Serial communication;
H) Timer unit
10. Now study the text to match examples with the proper paragraph and write the paragraph title in the blank:
a "stuck" program and
microcontroller’s max value
elapsed time can be determined by T1-T2 periods consideration
rules for information and fluent communication exchange
microcontroller recognition of the writing or reading processes
address transition from CPU memory and all blocks connection inside a microcontroller services
block with a built-in capability to operate with its contents
helps to get the contents of a
certain addressed location
main point definition and general idea introduction
1. _________________________________
Microcontroller integrates a number of the

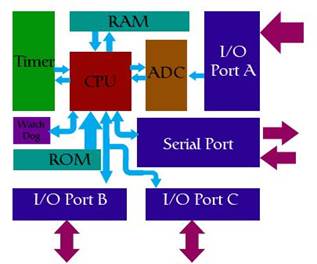
components of a microprocessor system onto a single microchip. It is optimized to interact with the outside world through on-board interfaces. Microprocessor is also used to co-ordinate the flow of information between separate memory and peripheral devices which are located outside. Connections to a microprocessor include address, control and data busses that allow selecting one of its peripherals and sending to or retrieve data from it. Microcontroller processor and peripherals are built on the same silicon and the devices are self-contained and rarely have any bus structures extending outside their packages. So a microcontroller incorporates onto the same microchip the CPU core, both ROM and RAM, some parallel digital I/O.

2. _________________________________
Memory is part of the microcontroller storing

data. For a certain input we get the contents of a certain addressed memory location. Memory consists of all memory locations, and addressing. Beside reading from a memory location, it must also provide for writing onto it. This is done by supplying an additional line called control line. We will designate this line as R/W (read/write). Control line is used in the following way: if r/w=1, reading is done, and if opposite is true then writing is done on the memory location.

3. _________________________________

The block that will have a built in capability to multiply, divide, subtract, and move their content from one memory location onto another is called "central processing unit" (CPU). Its memory locations are called registers. Registers are to help with performing various mathematical operations or any other operations with data wherever data can be found. Two independent entities (memory and CPU) which are interconnected, and thus any exchange of data is hindered, as well as its functionality. Simply stated, we must have some "way" through data goes from one block to another.

4. _________________________________

That "way" is called "bus". There are two types of buses: address and data bus. The first one consists of as many lines as the amount of memory we wish to address and the other one is as wide as data, in our case 8 bits or the connection line. First one serves to transmit address from CPU memory, and the second to connect all blocks inside the microcontroller. Thus we get a unit that's capable of working by itself, but it does not have

 2017-10-31
2017-10-31 213
213








