Productive efficiency is concerned with producing goods and services with the optimal combination of inputs to produce maximum output for the minimum cost.
To be productively efficient means the economy must be producing on its production possibility frontier. (i.e. it is impossible to produce more of one good without producing less of another).
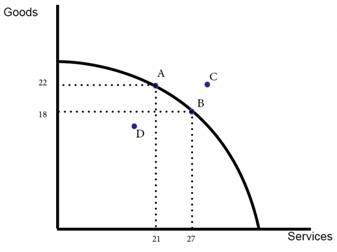
· Points A and B are productively efficient.
· Point D is inefficient because you could produce more goods or services with no opportunity cost
· Point C is currently impossible.
Economic efficiency is, roughly speaking, a situation in which nothing can be improved without something else being hurt. Depending on the context, it is usually one of the following two related concepts:
· Allocative or Pareto efficiency: any changes made to assist one person would harm another.
· Productive efficiency: no additional output can be obtained without increasing the amount of inputs, and production proceeds at the lowest possible average total cost.
Describe the difference between goods and services. Give your example.
Goods are items that are tangible, such as pens, salt, shoes, hats and folders
Services are activities provided by other people, such as doctors, lawn care workers, dentists, barbers, waiters, or online servers. According to economic theory, consumption of goods and services is assumed to provide utility (satisfaction) to the consumer or end-user, although businesses also consume goods and services in the course of producing other goods and services.
HISTORY
Physiocratic economists categorized production into productive labour and unproductive labour. Adam Smith expanded this thought by arguing that any economic activities directly related on material products (goods) were productive, and those activities which involved non-material production (services) were unproductive. This emphasis on material production was adapted by David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus and John Stuart Mill, and influenced later Marxian economics. Other, mainly Italian, 18th century economists maintained that all desired goods and services were productive.[1]
There are 5 workers on an enterprise. Each of them produces 300 goods. How many goods are produced on the enterprise?
5 x 300 = 1500 is maximum of the enterprise
 2018-02-13
2018-02-13 647
647








