Consider the situation where one of the mains phases (phase C) withdrew to ground via a relatively low resistance Rg, such as wire breakage and falling to the ground. The network diagrams (see Fig. 8.3), this fact will be reflected in parallel with YC conductivity Y g = 1/ R g (Y gis not shown). Consequently, between phase C and ground conductivity be YС + Y g. Accordingly, the expression (8.8) takes the form:
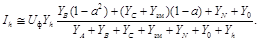 (8.21)
(8.21)
Three-phase four-wire network with earthed neutral:
Condition (8.9) is usually performed in the network, so the expression (8.21) can be simplified:
 (8.22)
(8.22)
Considering the relation (8.5), and R 0<< Rh we obtain:
 (8.23)
(8.23)
Three-phase three-wire network with isolated neutral:
For a thisnetwork YN = Y 0= 0. In addition, usually | YA|, | YB|, | YC |<< Yзм. Then the expression (19) takes the form:
 (8.24)
(8.24)
or, given the expressions for a and relations (8.5)
Ih=  U ph /(Rh + R g ) = U l/ (Rh + R g ). (8.25)
U ph /(Rh + R g ) = U l/ (Rh + R g ). (8.25)
In emergency mode, often have a situation in which Rg substantially more R0 and simultaneously Rg << Rh. Under this condition, a comparative analysis of the formulas (21) and (23) shows that a person is under tension Uc close to a linear network with isolated neutral, which is more dangerous than the network with earthed neutral, where Uc approaching the phase voltage. For both types of networks is characterized by a decrease in risk of electric shock by increasing the Rh.
 2020-07-01
2020-07-01 87
87








