| Abbreviation | Definition | Full term |
| ACL | A list of resources and the usernames of people who have a permitted access to those resources within a computer system. | |
| CIO | A network of computers that are connected over large distances. | |
| HTML | A protocol that allows Web pages, formatted in HTML, to be displayed on devices with small screens, such as PDAs and mobile phones. | |
| HTTP | A small, low- bandwidth Bluetooth network of up to 10 networks of eight devices each; used for tasks such as wireless synchronization of laptop computers with desktop computers and wireless printing from laptops, PDAs, or mobile phones. | |
| PAN | A unit within a company; is organized around a specific combination of product, distribution channel, and customer type. | |
| PDA | A handheld PC. It is a variety mobile device, which functions as a personal information manager. | |
| SBU | An organization’s top technology manager; responsible for overseeing all of the business’s information systems and related technological elements. | |
| URL | Names and abbreviations representing the IP address of a particular Web page. Contains the protocol used to access the page and the page’s location. Used in place of dotted quad notations. Universal ad package. | |
| WAN | The Internet protocol responsible for transferring and displaying Web pages. | |
| WAP | The language of the Internet; it contains codes attached to text that describe text elements and their relation to one another. |
Ex. 4.11. What are the products or/and processes most suitable to e-commerce? Give your reasons. Then read the text and do the assignment below.
Some products, such as books or CDs, are good candidates for electronic commerce because customers do not need to experience the physical characteristics of the particular item before they buy it. Because one copy of a new book is identical to other copies, and because the customer is not concerned about fit, freshness, or other such qualities, customers are usually willing to order a title without examining the specific copy they will receive. As technologies develop, many processes, which were strictly handled through traditional commerce, have become more suitable for electronic commerce. This trend will likely continue.
(From: Gary P. Schneider (2015) Electronic Commerce. (11th ed.). Cengage Learning. P.20-21)
Categorize the following processes by suitability for electronic commerce and traditional commerce.
1) Banking and financial services
2) Online delivery of software and digital content (music, movies, etc.)
3) Roommate-matching services
4) Sale of automobiles
5) Sale of books and CDs
6) Sale of goods with strong brand reputations
7) Sale of high-value jewelry and antiques
8) Sale of impulse items for immediate use
9) Sale of investment and insurance products
10) Sale of residential real estate
11) Sale of travel services
12) Sale of used, unbranded goods
| Well Suited to Electronic Commerce | Suited to a Combination of Electronic and Traditional Commerce Strategies | Well Suited to Traditional Commerce |
Ex. 4.12. Do you think it is easy for a business to shift to an online store? Why? Why not?
According to Digital River, building an e-commerce site is not as simple as ABC.
The findings by e-commerce company Digital River uncover a number of myths surrounding the venture into e-commerce. "By addressing these myths, companies will hopefully avoid landing themselves in hot water or losing unnecessary revenue."
(From: http://www.webdesignvn.com/ECommerce-Guide/F9EF868/Default.aspx)
Which of the following statements can be termed as e-commerce “myths”? Give your reasons.
1. A company becomes national as soon as it can accept credit cards and PayPal.
2. Aggressive marketing will create bad will with customers.
3. Building an e-commerce site does not enable businesses to trade easily.
4. Building an e-commerce site enables businesses to trade with no complications.
5. Businesses can market products aggressively online if they sell their products through a reseller.
6. Companies can sell directly to the SMB market via websites.
7. Companies cannot sell directly to the SMB market via websites.
8. Customers will stumble on a company's site easily; there is no need to do additional marketing or merchandising.
9. Ease of site navigation is a major factor.
10. Ease of site navigation is a minor factor.
11. E-commerce requires little outside input as it is a project for the IT department.
12. E-commerce is not a project for the IT department only and requires a lot of outside input.
13. E-commerce never boost the finances of any business.
14. E-commerce will boost the finances of any business.
15. Customers’ good will is created by aggressive marketing.
16. If businesses sell their products through a reseller, they cannot market products aggressively online.
17. Potential customers will assume that a company's site is illegitimate.
18. Potential customers will assume that a company's site is legitimate.
19. The moment a business can accept credit cards and PayPal, it becomes global.
20. To encourage customers to use a company's site it is necessary to do additional marketing or merchandising.
Ex. 4.13. Do you prefer to buy on-line or in shops? Give your reasons. Which goods are easier to buy on-line? Study the chart of an international survey below and discuss it with your partner.
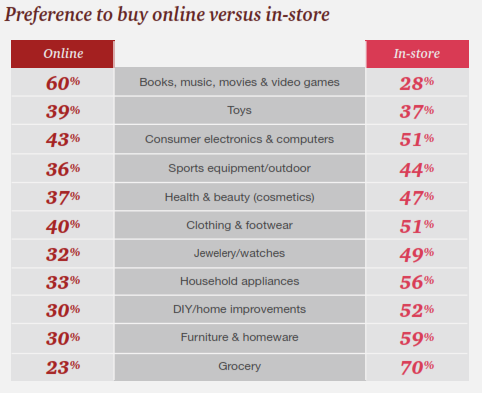
( From: www.pwc.com/2017totalretail)
 2020-10-10
2020-10-10 214
214