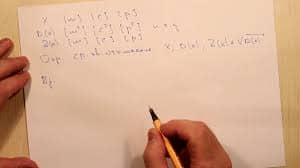Case 2
A patient is in a coma.
pH 7.17
pCO2 of 50 mm Hg.
SB 15,0 mmol / l
BB 38.0 mmol / l
-13 BE mmol / l
Ketone bodies - 250 micromoles (normal 140-200mkmol / l)
Titratable acidity - 270 ml / day (normal 70-100 ml / day)
Questions:
1. Rate the pH of arterial blood, indicate its degree (compensated, decompensated)
2. Make a conclusion about a type of ABB, justify the answer
3. Rate the value of indicators of ABB.
4. Explain compensatory mechanisms of ABB disorders of the patient
Case 3. A patient has a concussion, accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting and shortness of breath. Describe the violation of ABB of the patient. Explain the pathogenesis of changes.
pH 7.56
pCO2 of 26 mm Hg. Art.
SB 24,0 mmol / l
AB 17.0 mmol / l
BE 4.0 mmol / l
Questions:
1. Rate the pH of arterial blood, indicate its degree (compensated, decompensated)
2. Make a conclusion about a type of ABB, justify the answer
3. Rate the value of indicators of ABB. What is the cause of AB disorders
4. Explain compensatory mechanisms of ABB disorders of the patient
Case 4.
Patient has diffuse glomerulonephritis. Describe the violation of ABB of the patient.
pH 7.23
pCO2 of 34 mm Hg. Art.
SB 16,0 mmol / l
AB 13.0 mmol / l
EE - 11.0 mmol / l
Titratable acidity of urine: 8 ml of caustic (normally 70-100 ml / day)
Urine Ammonia: 8 mmol / l (normal range 20-50 mmol / l)
Questions:
1. Rate the pH of arterial blood, indicate its degree (compensated, decompensated)
2. Make a conclusion about a type of ABB, justify the answer
3. Rate the value of indicators of ABB. What is the cause of AB disorders
4. Explain compensatory mechanisms of ABB disorders of the patient
 2015-08-13
2015-08-13 282
282