A government budget is an annual financial statement presenting the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year that is often passed by the legislature, approved by the chief executive or president and presented by the Finance Minister to the nation. The budget is also known as the Annual Financial Statement of the country. This document estimates the anticipated government revenues and government expenditures for the ensuing (current) financial year.
The two basic elements of any budget are the revenues and expenses. Government expenses include spending on current goods and services, which economists call government consumption; government investment expenditures such as infrastructure investment or research expenditure; and transfer payments like unemployment or retirement benefits.
Expenditures authorized under a national budget are divided into two main categories. The first is the government purchase of goods and services in order to provide services such as education, health care, or defense. The second is the payment of social security and other transfers to individuals and the payment of subsidies to industrial and commercial companies. Both types are usually labeled “public expenditure,” and in many countries attention usually focuses on the aggregate of the two. This obscures important differences in the economic significance of the two items, however. The first represents the public sector’s claim on total national resources; the second the scale of its redistribution within the private sector.
Subject and functions of economic theory.
"Economic theory is the science of what a rare productive resources, people and society over time, with money or without their participation, elect for the production of various goods and distribute them for consumption in the present and the future, between different people and groups in society".
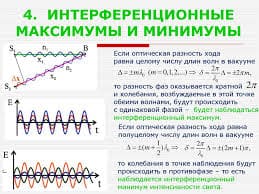
|
|
|
"The subject of economics - finding an effective use of scarce resources in the production of goods and services for the satisfaction of material needs."
Thus, the subject of economic theory is the work of people using limited resources to produce goods and services to meet their needs.
Economic theory performs methodological, practical, cognitive, predictive, educational and ideological functions.
Methodological function allows you to define economics as the basis for the development of a number of other economic disciplines (marketing, statistics, management, pricing).
Expression of the practical function of economic theory is the development of economic policy. In general, the practical function is the scientific foundation of economic policy, to identify principles and practices of good housekeeping.
Cognitive function is to comprehensively examine the forms of economic phenomena and their inner self, allowing you to discover the laws by which develops the national economy. This study begins by examining the facts of mass economic data, the behavior of economic agents that Western economic literature by the term "descriptive science."
The predictive function of economic theory is to determine the prospects for socio-economic development in the future. This function is related to the development of promising criteria and indicators. It has a special significance in the development of plans and forecasts for the national economy.
Educational function is manifested in the formation of economic thinking.
Types of costs: fixed cost and variable cost.
Costs are the money and other material expenditures incurred (привлеченные) in producing and selling goods during the period.
Fixed cost- costs that do not change with the amount of produced.
Fixed costs are costs that are independent of output. These remain constant throughout the relevant range and are usually considered sunk for the relevant range (not relevant to output decisions). Fixed costs often include rent, buildings, machinery, etc.
Variable costs are costs that vary with output. Generally variable costs increase at a constant rate relative to labor and capital. E.g. expenses for labour force wage, raw materials, packing expenses, stationary expenses, storage expenses, transportation expenses and others.
70) Pricing of the goods and average cost.
Price may be defined as the exchange of goods or services in terms of money. Without price there is no marketing in the society. If money is not there, exchange of goods can be undertaken, but without price; i.e., there is no exchange value of a product or service agreed upon in a market transaction, is the key factor which affects the sales operations.The market price of a product influences wages, rent, interest and profits. In other words, the price.of a product influences the price paid for the factors of production-labour, land, capital and entrepreneurship. The price is a matter of vital importance to the buyer and the seller. Exchange of the goods or services takes place only when the prices are agreed upon by the seller and the buyer.Price can decide the success or failure of a firm. Prices are important economic regulators. By transferring to money economy from barter economy, the importance of price has been increased. Price is a primary source of revenue which, all firms try to maximize by expanding markets.
|
|
|
Average cost- AC- is amount of money that is used in producing one unit of product.
Why is AC important for a businessman?
AC is foundation of price formation
AC helps to define price of a product.
P= AC+ addition (үстеме)
P= 20 tenge+5 tenge=25 tenge
Additions are profit sources. A profit maximizing firm must produce its output at minimum cost.
 2018-02-13
2018-02-13 833
833