Water crisis is a general term used to describe a situation where the available water within a region is less than the region's demand. The term has been used to describe the availability of potable water in a variety of regions by the United Nations and other world organizations. Others, for example the Food and Agriculture Organization, said in 2003 that there is no water crisis but steps must be taken to avoid one in the future. The major aspects of the water crisis are allegedly overall scarcity of usable water and water pollution.
The Earth has a limited supply of fresh water, stored in aquifers, surface waters and the atmosphere. Sometimes oceans are mistaken for available water, but the amount of energy needed to convert saline water to potable water is prohibitive today, explaining why only a very small fraction of the world's water supply derives from desalination.
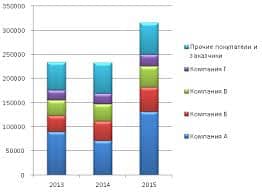
There are several principal manifestations of the water crisis:
inadequate access to safe drinking water for about 884 million people;
inadequate access to water for sanitation and waste disposal for 2.5 billion people;
groundwater overdrafting (excessive use) leading to diminished agricultural yields;
overuse and pollution of water resources harming biodiversity;
regional conflicts over scarce water resources sometimes resulting in warfare.
Waterborne diseases and the absence of sanitary domestic water are one of the leading causes of death worldwide. For children under age five, waterborne diseases are the leading cause of death. At any given time, half of the world's hospital beds are occupied by patients suffering from waterborne diseases. According to the World Bank, 88 percent of all waterborne diseases are caused by unsafe drinking water, inadequate sanitation and poor hygiene.
Грамматический справочник с упражнениями
 2015-06-28
2015-06-28 484
484