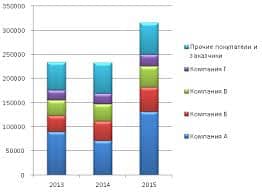
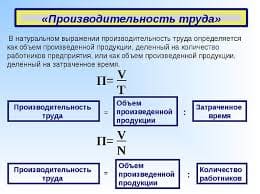
Fellow-students
Text 1
Energy conservation is the practice ___ decreasing the quantity ___ energy used while achieving a similar
outcome ___ end use. This practice may result ___ increase ___ financial capital, environmental value,
national security, personal security, and human comfort. Individuals and organizations that are direct
consumers ___ energy may want to conserve energy ___ order to reduce energy costs and promote
economic, political and environmental sustainability. Industrial and commercial users may want to increase
efficiency and thus maximize profit.
___ a larger scale, energy conservation is an important element ___ energy policy. ___ general, energy
conservation reduces the energy consumption and energy demand per capita, and thus offsets the growth
___ energy supply needed to keep ___ ___ population growth. This reduces the rise ___ energy costs, and
can reduce the need ___ new power plants, and energy imports. The reduced energy demand can provide
more flexibility ___ choosing the most preferred methods ___ energy production.
___ reducing emissions, energy conservation is an important part ___ lessening climate change. Energy
conservation facilitates the replacement ___ non-renewable resources ___ renewable energy. Energy
conservation is often the most economical solution ___ energy shortages, and is a more environmentally
benign alternative ___ increased energy production.
The U.S. is currently the biggest consumer ___ energy in the world, although ___ current levels ___ growth,
it is possible that ___ the future China could become the leading energy consumer. The U.S. Department
___ Energy categorizes national energy use ___ four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial,
and industrial.
Energy usage ___ the transportation and residential sectors (about half ___ U.S. energy consumption) is
largely controlled ___ individual domestic consumers. Commercial and industrial energy expenditures are
determined ___ businesses entities and other facility managers. National energy policy has a significant
effect ___ energy usage across all four sectors.
The transportation sector includes all vehicles used ___ personal or freight transportation. ___ the energy
used ___ this sector, approximately 65% is consumed ___ gasoline-powered vehicles, primarily personally
owned. Diesel-powered transport (trains, merchant ships, heavy trucks, etc.) consumes ___ 20%, and air
traffic consumes most ___ the remaining 15%.
Text 2
The oil supply crises ___ the 1970s spurred the creation, ___ 1975, ___ the federal Corporate Average Fuel
Economy (CAFE) program, which required auto manufacturers to meet progressively higher fleet fuel
economy targets. The next decade saw dramatic improvements ___ fuel economy, mostly the result ___
reductions ___ vehicle size and weight. These gains eroded somewhat after 1990 due ___ the growing
popularity ___ sport utility vehicles, pickup trucks and minivans, which fall ___ the more lenient "light truck"
CAFE standard.
___ addition ___ the CAFE program, the U.S. government has tried to encourage better vehicle efficiency
___ tax policy. Since 2002, taxpayers have been eligible ___ income tax credits ___ gas/electric hybrid
vehicles. A "gas-guzzler" tax has been assessed ___ manufacturers since 1978 ___ cars ___ exceptionally
poor fuel economy. While this tax remains ___ effect, it currently generates very little revenue as overall fuel
economy has improved.
Another focus ___ gasoline conservation is reducing the number ___ miles driven. An estimated 40% of
American automobile use is associated ___ daily commuting. Many urban areas offer subsidized public
transportation to reduce commuting traffic, and encourage carpooling ___ providing designated highoccupancy
vehicle lanes and lower tolls ___ cars with multiple riders.
___ recent years telecommuting has also become a viable alternative ___ commuting ___ some jobs, but as
of 2003 only 3.5% ___ workers were telecommuters. Ironically, hundreds ___ thousands ___ American and
European workers have been replaced ___ workers ___ Asia who telecommute from thousands ___ miles
away.
A vehicle's gas mileage normally decreases rapidly ___ speeds above 55 miles ___ hour. A car or truck
moving ___ 55 miles an hour can get about 15 percent better fuel economy than the same car going 65 mph.
According ___ the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), as a rule ___ thumb, each 5 mph you drive over 60
mph is similar ___ paying an additional $0.21 ___ gallon ___ gas (at $3.00 ___ gallon).
The industrial sector represents all production and processing ___ goods, including manufacturing,
construction, farming, water management and mining. Increasing costs have forced energy-intensive
industries to make substantial efficiency improvements in the past 30 years. For example, the energy used to
produce steel and paper products has been cut 40% ___ that time frame, while petroleum/aluminum refining
and cement production have reduced their usage ___ about 25%. These reductions are largely the result
___ recycling waste material and the use ___ cogeneration equipment for electricity and heating.
The energy required ___ delivery and treatment ___ fresh water often constitutes a significant percentage
___ a region's electricity and natural gas usage (an estimated 20% ___ California's total energy use is waterrelated.
___ light of this, some local governments have worked toward a more integrated approach ___
energy and water conservation efforts.
Unlike the other sectors, total energy use ___ the industrial sector has declined ___ the last decade. While
this is partly due to conservation efforts, it's also a reflection ___ the growing trend ___ U.S. companies to
move manufacturing operations offshore.
Text 3
The commercial sector consists ___ retail stores, offices (business and government), restaurants, schools
and other workplaces. Energy ___ this sector has the same basic end uses as the residential sector, ___
slightly different proportions. Space conditioning is again the single biggest consumption area, but it
represents only ___ 30% ___ the energy use ___ commercial buildings. Lighting, at 25%, plays a much
larger role than it does ___ the residential sector. Lighting is also generally the most wasteful component ___
commercial use. A number ___ case studies indicate that more efficient lighting and elimination ___ overillumination
can reduce lighting energy ___ approximately fifty percent ___ many commercial buildings.
Commercial buildings can greatly increase energy efficiency ___ thoughtful design, with today's building
stock being very poor examples ___ the potential ___ systematic (not expensive) energy efficient design.
Commercial buildings often have professional management, allowing centralized control and coordination
___ energy conservation efforts. As a result, fluorescent lighting (about four times as efficient as
incandescent) is the standard ___ most commercial space, although it may produce certain adverse health
effects.
Potential health concerns can be mitigated ___ using newer fixtures ___ electronic ballasts rather than older
magenetic ballasts. As most buildings have consistent hours ___ operation, programmed thermostats and
lighting controls are common. However, too many companies believe that merely having a computer
controlled Building automation system guarantees energy efficiency. As an example one large company ___
Northern California boasted that it was confident its state ___ the art system had optimized space heating. A
more careful analysis ___ Lumina Technologies showed the system had been given programming
instructions to maintain constant 24 hour temperatures ___ the entire building complex. This instruction
caused the injection ___ nighttime heat into vacant buildings when the daytime summer temperatures would
often exceed 90 degrees Fahrenheit. This mis-programming was costing the company ___ $130,000 per
year ___ wasted energy. Many corporations and governments also require the Energy Star rating for any
new equipment purchased ___ their buildings.
Solar heat loading ___ standard window designs usually leads ___ high demand ___ air conditioning ___
summer months. An example ___ building design overcoming this excessive heat loading is the Dakin
Building ___ Brisbane, California, where fenestration was designed to achieve an angle ___ respect ___ sun
incidence to allow maximum reflection ___ solar heat; this design also assisted ___ reducing interior overillumination
to enhance worker efficiency and comfort.
 2015-10-14
2015-10-14 388
388