Collective nouns denote a number or collection of similar individuals or things as a single unit.
Collective nouns fall into the following groups:
a. nouns used only in the singular and denoting a number of things collected together and regarded as a single object:
e.g. It was not restful, that green foliage. (London)
b. nouns which are singular in form though plural in meaning: police, poultry, cattle, people, gentry. They are usually called nouns of multitude. These nouns are used with a verb in plural.
e.g. The cattle are in the field now.
The police have already arrested the suspect.
☼ Note: Police is a state organization.
c. nouns that may be both singular and plural: family, crowd, fleet, nation. We can think of a number of crowds, fleets or bastions as well as of single crowd, fleet. The word family with a verb in singular is used to denote a social unit. When we use ‘ family’ with a verb in plural we mean each member of this social unit.
e.g. From his place he saw crowds of people gathering in the street for meeting.
The family were all asleep when I came home.
Nouns of material denote material: iron, silver, tea, water, paper. They are uncountable nouns and are generally used without any article.
e.g. There was coffee in the cup. It was still warm.
Silver is won in that mine outside the town.
We can sometimes use the nouns of material in the plural form to denote different sorts or kinds of a given material.
e.g. There is a great variety of select wines in this shop.
(wines – different sorts of wine.)
Nouns of material may turn into class nouns and become countable nouns when they come to express an individual object of definite shape.
Compare: There was no glass in the windows. That’s why it was so
cold in the room.
He came in the bar and ordered a glass of ginger ale.
The best coffee is produced in Brazil.
“Two teas and a coffee, please!” (Two cups of tea
and one cup of coffee)
The more complete semantic classification of nouns in English can be seen in the following scheme 1:
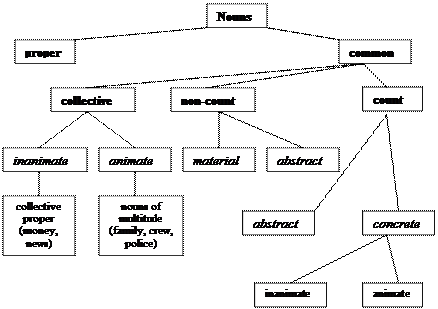
 Scheme 1
Scheme 1

 1.2 According to the morphological composition nouns can be divided into simple, derived (derivatives) and compound.
1.2 According to the morphological composition nouns can be divided into simple, derived (derivatives) and compound.
Simple nouns have neither prefixes nor suffixes and consist of only one root – morpheme: room, half, chair, hat, train.
Derived nouns (derivatives) are nouns which have derivative elements, either prefix or suffix or both: reader, impatience, symbolism, childhood, misunderstanding.
The main noun-forming suffixes are those forming abstract nouns and those forming concrete, personal nouns.
 2017-10-25
2017-10-25 295
295








