84  Electronic Engineering
Electronic Engineering

 SPECIALIST READING A: Digital Signal Processing
SPECIALIST READING A: Digital Signal Processing

8. Scan the text and match the headings (a – f) with the paragraphs (1 – 5). There is one extra heading you will not need to use.
s) How signals are treated;
t) DSP fundamentals;
u) DSP hardware;
v) DSP application fields;
w) The history of DSP;
x) DSP technology;
9. Now study the text to find this information.
DSP subfields
DSP goal
Sampling stages
DSP advantages
DSP studying
domains
Specific DSP
applications
1. _________________________________
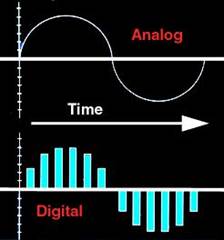
Digital signal processing (DSP) is concerned with

the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. Digital signal processing includes subfields like: audio and speech signal processing, sonar and radar signal processing, sensor array processing, spectral estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, signal processing for communications, control of systems, biomedical signal processing, seismic data processing, etc.

2. _________________________________

With the increasing use of computers the usage of and need for digital signal processing has increased. In order to use an analog signal on a computer it must be digitized with an analog-to-digital converter. Hence the goal of DSP is to measure, filter and/or compress continuous real-world analog signals. The first step is usually to convert the signal from an analog to a digital form, by sampling it, which turns the analog signal into a stream of numbers. To convert analog signals into digital ones, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is applied. Sampling is usually carried out in two stages, discretization and quantization. In the discretization stage, the space of signals is partitioned into equivalence classes and quantization is carried out by replacing the signal with representative signal of the corresponding equivalence class. In the quantization stage the representative signal values are approximated by values from a finite set. The Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem states that a signal can be exactly reconstructed from its samples if the sampling frequency is greater than twice the highest frequency of the signal; but requires an infinite number of samples. In practice, the sampling frequency is often significantly more than twice that required by the signal's limited bandwidth.

However, often, the required output signal is another analog output signal, which requires a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). Even if this process is more complex than analog processing and has a discrete value range, the application of computational power to digital signal processing
 2017-10-31
2017-10-31 272
272