The shape of a tree depends on many factors, such as the amount of space it has to grow in, the amount of sunshine and moisture it receives, the relative growth rate of its terminal and lateral branches, and any damage it receives from such factors as lightning, fires, prevailing winds, snow, animals, and disease. The part of the tree above the trunk, called the crown, is built up bit by bit and year by year in order to maximize the leaves’ exposure to the sun’s energy. The direction of growth of the branches is towards the light. Trees that can reach above their neighbours get the most sunshine and are said to have dominant crowns. Those that are shaded by other trees may be slower growing and are called suppressed trees. In some species, such as poplar, continued shading over several years will eventually lead to their death. Other species, however, called shade tolerant, can survive long periods in low levels of light. Species such as white spruce establish themselves under a canopy and eventually become dominant as pioneer species die off. While a great height and large crown give a tree more exposure to sunlight, they make the branches more vulnerable to damage from severe winds or heavy snow. To balance the spread of its branches, a tree tends to grow deeper roots to anchor it firmly against toppling by storms. The jack pines have large deep taproots which enable them to root themselves well in shallow sandy soils and access water. Spruce trees have a shallow root network which leaves the trees susceptible to wind blow when the tree is exposed. Such exposure may come from removal of adjacent trees during logging operations or when a road is being built or, naturally when a fire leaves a strip of trees along a lake as it goes through an area.
The crown, which consists of the leaves and branches at the top of a tree, plays an important role in filtering dust and other particles from the air. It also helps cool the air by providing shade and reduces the impact of raindrops on the soil below.
Leaves are food factories of the tree. Powered by sunlight, the green substance in leaves, called chlorophyll,uses carbon dioxide and water to produce life-sustaining carbohydrates.
The entire process is called photosynthesis. Leaves are also responsible for respiration and transpiration. A tree’s leaf is one major marker that Most trees can be identified by the leaf alone helps in keying out and identifying any species of tree. Leaves arrangement vary in shape, sizeand arrangement.
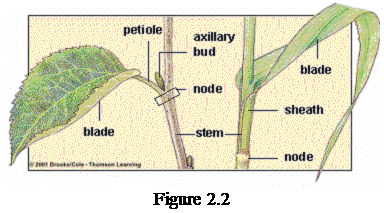
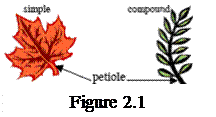 The leaves have two main parts, a blade and a petiole (figure 2.2). Leaves can be of many different shapes. Primarily, leaves are divided into simple – a single leaf blade and compound – a leaf with more than one blade (figure 2.1).
The leaves have two main parts, a blade and a petiole (figure 2.2). Leaves can be of many different shapes. Primarily, leaves are divided into simple – a single leaf blade and compound – a leaf with more than one blade (figure 2.1).
All blades are attached to a single leaf stem. Where the leafstem attaches to the twig there is a bud (figure 2.2).
Leaves may be arranged on the stem either in an alternate arrangement – leaves that are staggered or not placed directly across from each other on the twig; or in an opposite arrangement – 2 or 3 leaves that are directly across from each other on the same twig (figure 2.3).
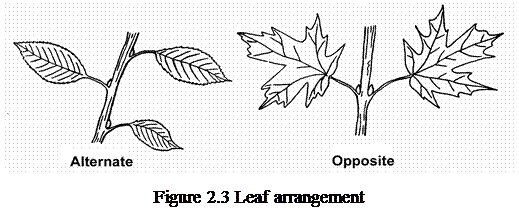
Leaves may be arranged on the stem either in an alternatearrangement – leaves that are staggered or not placed directly across from each other on the twig; or in an opposite arrangement – 2 or 3 leaves that are directly across from each other on the same twig (figure 2.3).
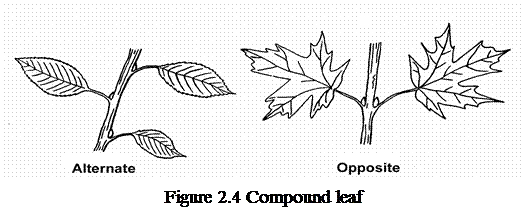
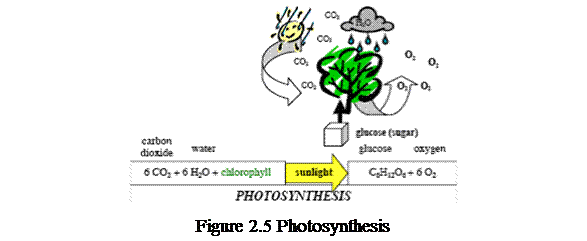
Compound leaves may be palmate – having the leaflets arranged round a single point like fingers on the palm of a hand; pinnate – when the leaves are joined on thetwo sides of the stalk, like the vanes of a feather or doubly – compound (figure 2.4). The form of leaves is related with all their functions and their environment. In addition to photosynthesis (figure 2.5), the leaf also carries out all the other exchanges with the atmosphere. It is through the leaf that the plant «breathes» (absorbs oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide plus energy) and transpires.
2.3Find the answers to the following questions in the text 1:
1. What is a crown?
2. Which trees have dominant crowns?
3. Which trees are called suppressed ones?
4. A leaf consists of two parts. What are they?
5. Where are buds situated?
2.4 Give synonyms to the following words using the text 1: form, humidity, a number of, atmosphere, taking away, injure, great, achieve, on the whole, harsh.
2.5 Complete the sentences with the following words: twigs, leaves, shapes, trunk, bark.
Trees come in various … and sizes but all have the same basic structure. They have a central column called the …. The … – covered trunk supports a framework of branches and …. This framework is called the crown. Branches in turn bear an outside covering layer of ….
 2017-11-01
2017-11-01 394
394








