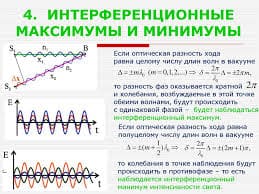
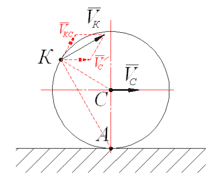
Painting after 1790 tended more toward ROMANTICISM, especially in landscape, where a bold style and an intense feeling for the moods of nature, demonstrated in the art of J. M. W. Turner, John Constable, and many others, made the English school of landscape painting the most vital in Europe. The visionary art of William Blake is another manifestation of romanticism. The fame of English art after the fall of Napoleon in 1815 is shown by the flattering reception of Sir Thomas Lawrence when he toured the Continent to paint the victorious allied sovereigns, generals, and statesmen.
Victorian art, backed by continuing economic prosperity and an expanding middle class, represents an almost equally vigorous development, even though it was less in touch with the Continent than 18th-century art had been. It found its main architectural expression in the Gothic Revival, seen in a renewal not only of church building but also in railway stations, such as Saint Pancras (begun 1860) in London, by Sir George Gilbert Scott, town halls, and the Houses of Parliament (begun 1836) by Sir Charles Barry and Augustus Pugin. The Crystal Palace by Sir Joseph Paxton, built of iron and glass in sections erected on site, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851 in Hyde Park, London, was an historically significant development.
Victorian popular painting consisted mainly of domestic and historical scenes charged with sentiment and telling an affecting story, but the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, founded in 1848 by Holman Hunt, Sir John Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, and others, made more serious claims. These artists sought to combine the pure, unaffected spirit of the Italian artists before Raphael with a meticulous Realism.
***
14
After 1860, Pre-Raphaelitism became dreamier, suffused with a nostalgia for the Middle Ages, and merged with the Arts and Crafts Movement led by William Morris. The late 19th century also produced one other artist of international importance, the Scottish architect and designer Charles Rennie Mackintosh, whose Glasgow School of Art (1898-99) is perhaps the last building of real distinction erected in the British Isles. The recent revival of interest in architecture has brought the work of Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens back to prominence, particularly his romantic country houses and his enormous neo-classic Viceroy's House (1913-31; now President's House) in New Delhi, India.
Contemporary Period
National decline began to set in around 1900, and English artists have spent the 20th century in a well-meaning attempt to catch up with international developments. They have adopted one by one the "isms" of the modem movement, beginning with Impressionism, but always a few years behind and always in a diluted form. Among modern artists, however, the two dominant characteristics of English art — the romantic tradition and the emphasis on line — may be seen in the sculpture of Henry Moore and the painting of Francis Bacon, David Hockney, and Graham Sutherland. Coventry Cathedral by Sir Basil Spence was disliked by many critics but has found favour with the public. Of the work of contemporary British architects, that of James Frazer Stirling has perhaps been the most influential.
 2018-02-20
2018-02-20 283
283