Answering WHY questions: Speak up your mind.
1. Why must nations consider trade-offs when deciding what to produce?
2. Why does an economic system have to decide for whom to produce?
3. Why might people’s material well-being rarely improve in a traditional economy?
4. Why can’t businesses or nations produce as much as they want?
5. Why might a market economy be described as the “opposite” of a command economy?
6. Why don’t “pure economic systems” exist?
7. In a mixed economy, why might the government have to regulate businesses in order to protect the environment?
Reviewing: Watch video “Types of Economic Systems”. Have you learnt anything new? Be ready to answer the following questions:
1. Can there be a market economy without government involvement?
2. How is a mixed economy defined?
3. What kind of balance does a mixed economy try to find?
Critical thinking (Discussion competency): Discuss the following questions in groups/pairs.
(1) Write down your opinion in note form;
(2) Prepare for discussion: revise the speech formulas.
1. What basic economic question depends on a nation’s available natural resources?
2. What economic question is being answered if an industry replaces some workers with machines?
3. Do you think it’s fair that some people have more than others, or should everyone share equally in what a society produces?
Exploring issues: Socialism can be defined as an economic system that stresses government ownership of the major factors of production and control of the distribution of goods.
Study the list of characteristics and tick the ones that could concern pure socialism:
· Most prices are set by the state, rather than by forces of demand and supply.
· The movement of resources, particular labor, is strictly controlled. The central planning authority makes all decisions.
· The government lets people and businesses make their own economic decisions without government interference.
· Most of the major factors of production are owned by the state. Private property rights are strictly limited to small tools that an individual needs for an occupation.
· People living and working in these economies rarely experience an increasing level of material well-being.
· Individual risk taking is not allowed. The state takes all of the risk when it decides which new companies shall be formed.
· Economic decisions about what, how and for whom to produce are all made by the state officials through central planning agencies.
· Taxation is often used to redistribute income.
· The government places certain legal restrictions on freedom of enterprise.
Solving problems and finding solutions: In Russia’s economy, people’s career choices determine their level of income, which in turn affect their ability to purchase produced goods. Do you think goods and services should be distributed in a way other than based on income? Explain your answer.
Making comparisons: Research Russia’s economy today and when it was a command economy under the Soviet Union. Prepare a chart listing the similarities and differences in how the three basic economic questions were and are answered under both economies.
Summarizing: Summarize what you’ve learned so far about economic systems. Note that all economic systems are based on the model below. The model shows how an economic system must make decisions based on the concept of scarcity. Each society’s system must make economic choices by answering the three key economic system questions while making the best use of limited resources.
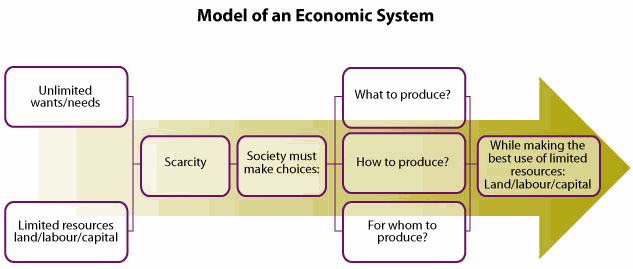
Applying information (Team work competency): Each nation has a different economic system, or an organized way in which it uses its resources to satisfy people’s needs and wants. But all economic systems address the same three basic questions. Work with your group to complete the chart below and create your own economic system to answer these questions.
| TYPE | EXAMPLE COUNTRIES | STRENGTHS | WEAKNESSES | POSSIBLE IMPROVEMENTS |
Follow the following steps:
1. Individual work. Identify types of economic systems, note the countries that exemplify each system and record the strengths and weaknesses of each type.
2. Paired work. Create a list of improvements or alternative ways of handling
resources for each system.
3. Group work. Work in groups of four. Pairs share their findings with the group. Complete the chart with answers agreed upon.
4. Group work/analysis. Create a model economic system that incorporates the strengths of the systems included in the chart as well as the recommendations for improvements. Brainstorm the name for the system. Prepare a written description of the system’s characteristics and indicate how it deals with the basic questions. Share your description with the class.
Enjoying comprehension competency focus:
 2020-06-29
2020-06-29 104
104