ANATOMY OF A TOOTH
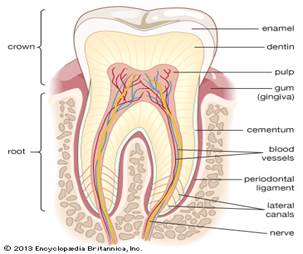
Every tooth consists of a crown, a neck and one or more roots. The crown is the part visible in the mouth and the root is the part hidden inside the jaw. The junction of crown and root is called the neck and the end of the root is called the apex. Every tooth is composed of enamel, dentine, cementum and pulp.
Enamel. This is the outer covering of the crown and is the hardest substance in the body. It is insensitive to pain. Unlike most other body tissues it cannot undergo repair; thus any damage caused by decay or injury is permanent. The microscope shows that it consists of long solid rods, called enamel prisms, cemented together by the interprismatic substance. The prisms run roughly at right angles to the surface.
Dentine. It is situated under enamel andoccupies the interior of the crown and root. It is very sensitive to pain. It is attacked by caries when the protective enamel has been lost. Dentine from elephants’ tusks is commonly known as ivory but is exactly the same dentine as that found in human teeth.
Cementum. This is the outer covering of the root and is similar in structure to bone. Cementum meets enamel at the neck of the tooth.
Pulp. Pulp is the most vital part of the tooth. Unlike enamel, dentine and cementum, the pulp is purely soft tissue. It contains blood vessels and nerves, and occupies the center of the dentine. Vessels and nerves of the pulp enter the root apex through the apical foramen and pass up the root canal into the crown, where the space occupied by the pulp is called the pulp chamber. The nerves of the pulp are responsible for pain felt when dentine is drilled or toothache occurs. Pulp acts as a security and alarm system for a tooth. The pulp has several functions, such as:
Sensory Function - Pain from trauma to pulp, differences in temperature, and pressure are caused by stimulation of the pulp.
Formation of Dentin - The pulp is responsible for the formation of dentin. In response to trauma, the pulp forms secondary dentin.
Nourishment - The pulp contains blood vessels that transport nutrients to the roots of the teeth.
Supporting Structures. Every tooth is inserted into the jaw by its root. The part of the jaw containing the teeth is known as the alveolar process1 and is covered with a soft tissue called gum. The jaw bones consist of a dense outer layer known as compact bone2 and a softer interior called spongy bone3.
A tooth is attached to its socket in the jaw by a soft fibrous tissue called the periodontal membrane. It acts as a shock absorber and is attached to the cementum of the root and the compact bone lining the socket. The periodontal membrane contains nerves and blood vessels, but consists mainly of bundles of fibers which pass obliquely from cementum to bone.
1alveolar process — альвеолярний відросток
2compact bone — компактна речовина
3spongy bone — губчаста кістка
Exercise 6. Match the translation of the English and Ukrainian word-combinations.
| a) apical foramen | 1) верхівковий отвір |
| b) spongy bone | 2) губчата кістка |
| c) sensitivity to pain | 3) чутливість до болю |
| d) purely soft tissue | 4) цілковито м’яка тканина |
| e) undergo repair | 5) піддаватися відновленню |
| f) alveolar process | 6) альвеолярний відросток |
| g) a dense outer layer | 7) щільний зовнішній шар |
| h) a shock absorber | 8) амортизатор |
 2020-09-24
2020-09-24 1641
1641








