In Excel, you can copy data from one area of a worksheet and place the data you copied anywhere in the same or another worksheet. In other words, after you type information into a worksheet, if you want to place the same information somewhere else, you do not have to retype the information. You simple copy it and then paste it in the new location.
You can use Excel's Cut feature to remove information from a worksheet. Then you can use the Paste feature to place the information you cut anywhere in the same or another worksheet. In other words, you can move information from one place in a worksheet to another place in the same or different worksheet by using the Cut and Paste features.
Microsoft Excel records cell addresses in formulas in three different ways, called absolute, relative, and mixed. The way a formula is recorded is important when you copy it. With relative cell addressing, when you copy a formula from one area of the worksheet to another, Excel records the position of the cell relative to the cell that originally contained the formula. With absolute cell addressing, when you copy a formula from one area of the worksheet to another, Excel references the same cells, no matter where you copy the formula. You can use mixed cell addressing to keep the row constant while the column changes, or vice versa.
Show properties of operating systems.
Properties of OS
An operating system (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. The operating system is a vital component of the system software in a computer system.
The essential properties of operating systems are:
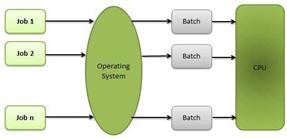
Batch processing
Batch processing is a technique in which an Operating System collects the programs and data together in a batch before processing starts.


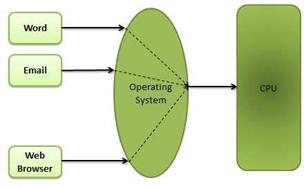
Multitasking
Multitasking is when multiple jobs are executed by the CPU simultaneously by switching between them. Switches occur so frequently that the users may interact with each program while it is running.


Multiprogramming
Sharing the processor, when two or more programs reside in memory at the same time, is referred as multiprogramming. Multiprogramming assumes a single shared processor. Multiprogramming increases CPU utilization by organizing jobs so that the CPU always has one to execute.
The following figure shows the memory layout for a multiprogramming system.

Real Time System
Real-time systems are usually dedicated, embedded systems. An operating system does the following activities related to real-time system activity.
· In such systems, Operating Systems typically read from and react to sensor data.
· The Operating system must guarantee response to events within fixed periods of time to ensure correct performance.
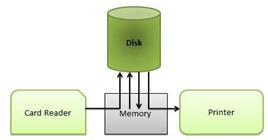
Spooling
Spooling refers to putting data of various I/O jobs in a buffer. This buffer is a special area in memory or hard disk which is accessible to I/O devices.
 2018-02-20
2018-02-20 261
261