During the process of research the following scientific methods were used: theoretical level, historical, logical, analysis, observation, comparison, induction, innovative and graphical representation of the results.
3.Results.
The article presents the materials to understand the need to create boats that meet the urgent needs of mankind in the development of the oceans. Rapidly developing technological progress involves the creation of a new generation of different types of vessels, improving their technical condition on the basis of the latest achievements of science and technology, the introduction of nanotechnology in the production and equipment of ships, boats.
From rafts made of logs and boats carved from tree trunks, shipbuilding has evolved to nuclear submarines and icebreakers. Humanity is not standing still, constantly improving the floating system for use in life (Fedorov, 2018).
Today, the shipbuilding industry receives orders for the construction of specialized ships – cruise liners, supply vessels (gas carriers, container ships), tanker and bulk fleets, powerful nuclear icebreakers to develop the Arctic. All these points contribute to the development of scientific and technical potential, the increase in the number of patents and the improvement of innovative works of civil orientation. Even such boats as pontoons have undergone a lot of changes in recent years.
The pontoon is a flotation device for maintaining a weight in the water (Wikipedia). Bottom grid is a bearing surface of plastic, coupled with a pontoon. It has a cross section in the direction of water flow profiled shape and is designed to create a hydraulic and aerodynamic lift. Plastic pontoon structures are composed of bottom grids and pontoons of a new kind, different from the existing pontoons in its technical characteristics due to the materials and form of manufacture that extend the scope and use of these vessels in the commercial, military, scientific, sporting and other purposes. Plastic pontoon structures are various in form, multi-tiered, prefabricated floating structures that form a coastal zone or an island of bottom gratings and pontoons resting on the water surface, with supporting structures located on the water, above the water, under the water. They may be private property or property relating to the fixed assets of the shipping company, with the legal regime established by law.
In the age of plastic American and Russian inventors patented a number of inventions of plastic floating means-pontoons. On the basis of these inventions created a variety of plastic pontoon structures used for berths of light ships and beach holidays. But no matter how hard the inventive idea, to date, innovative approaches to safe (from waves) the human presence in the ocean was not undertaken. In addition to submarines are able to stay under water below the level of passage of the wave, the vessels are doomed to suffer and to struggle constantly with the waves and winds.
Monitoring of coastal processes in the development of environmental protection measures reveals the increasing destruction of the coastal zone, the development of natural and man-made processes, the activation of coastal abrasion. The water element, in the form of storm waves cuts the bases of coastal breakages, forming landslides, landslides and talus. Waves and wind constantly damage the coastline of the Black and Azov seas. The rise of the sea level greatly accelerates the rate of coastal destruction. Very effective in the world, domestic practice of protection of sea shores is the creation of free beaches (Vostrikov, 2006).
Plastic pontoon structures of the new generation are able to protect coastal areas from abrasion and destruction of the coast. Specially equipped pontoon structures can receive energy from solar panels and from coastal waves at the time of crossing the waves of the splash line and falling into the pool. From plastic pontoons with bottom lattices it is possible:
to build a whole island with housing for people;
- to grow gardens, create cottages, farm buildings on water and under water;
- to create permanent scientific expedition bases for the study of climatic, meteorological and other interesting parameters of the ocean sphere;
- use in gas and oil production, fish farming and fishing.
In line with the Algorithmics of innovative development from the notification of public authorities on the availability of the investment project of plastic pontoon structures and the need for its implementation, the progress of success is influenced by scientific implementation cycles (Velichko, 2015). The possibility of using the advanced technical capabilities of pontoons in the market mechanism, to solve the urgent problems of people, the main place is occupied by the progressiveness and novelty that determine the demand and sales of products in the national economy. The demand for plastic pontoon structures is explained by a wide range of their application in various sectors of the economy, low cost and increased safety of being on the water surface, provided by the method of their production, shape and material.
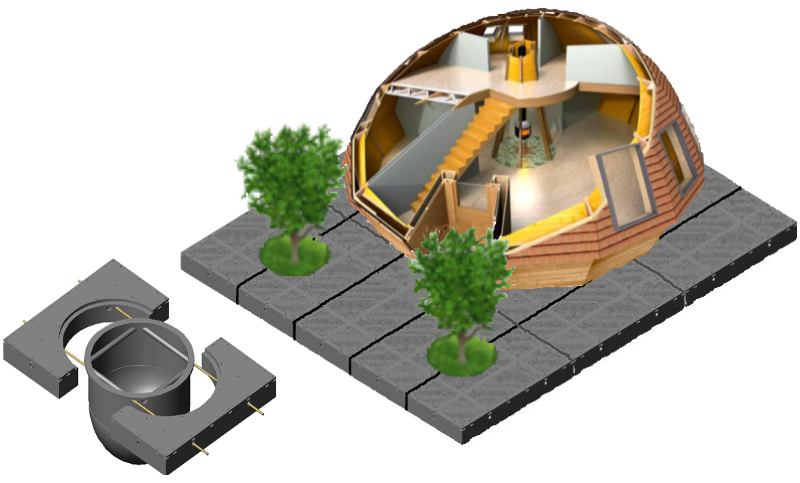

Figure 1. Structural features of plastic pontoon system, cable connection.
Two pontoons allow the Apple tree to grow on the water (figure 1). To live, we can use pontoons instead of land. Entire cities can be built on plastic pontoon structures (figure 2). The internal structural structure of the pontoon provides the presence of conductive, ventilation and plumbing systems. Pontoons, based on the surface of the water, are a kind of basis (Foundation), for the location, fixing the supporting structures on the pontoons and under the pontoons, in the water. Cast pontoon body allows you to provide and create a variety of technical forms, holes and devices made of plastic, in its manufacture. The ability to tier (multi-layer) Assembly increases the load capacity of the structure and its strength. Such technical capabilities of pontoons will provide social needs and comfortable conditions for people on the sea surface.
It is known that penetration into the ocean depths is as difficult and dangerous as the conquest of outer space. And the possibility of safe deployment and long-term stay of a person in the ocean, being in enterprises near their own homes, will remove some of the issues facing humanity due to lack of mineral resources, lack of energy, food.
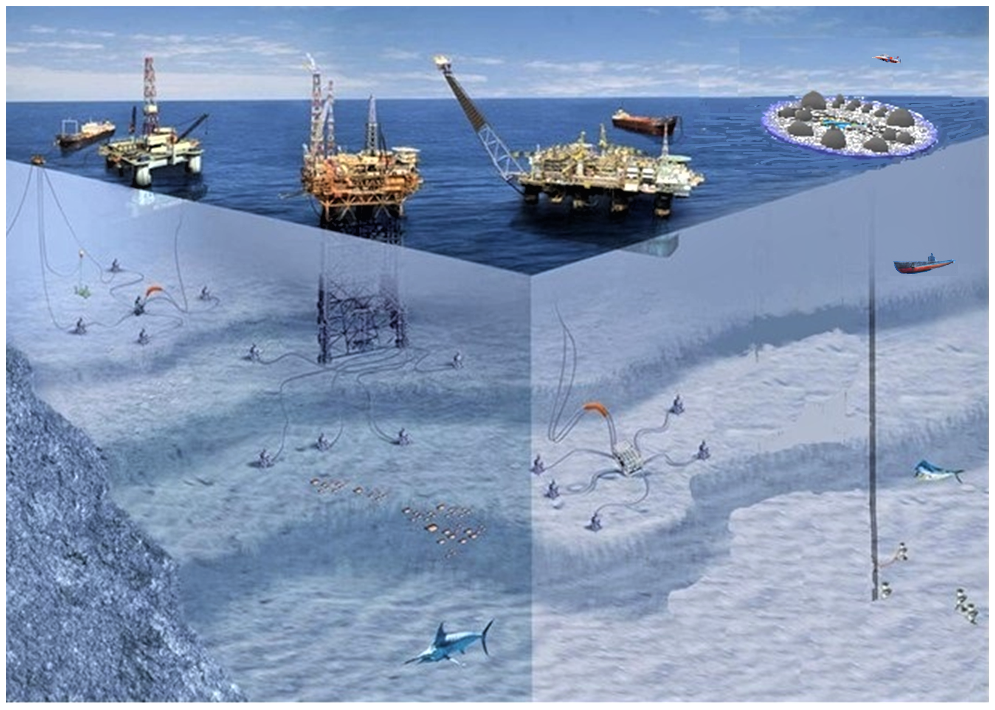

Figure 2. Model of plastic pontoon system in the open ocean.
The ability to move quickly, mobility is provided by aircraft and submarines. This is especially important in emergency situations, the need for medical care. Plastic pontoon structures are able to ensure the landing of light motor aircraft now. The use of nanotechnology will allow to create pontoon airfields in the ocean. If you know and follow the laws of nature, a person can live on the water without fear of large tsunamis and storms. And the construction of domed housing and premises above the water surface significantly reduces the harmfulness of hurricanes and strong winds. Even icebergs that could sink, in the blink of an eye, such a ship as the Titanic, are not so dangerous for the Islands of pontoon plastic structures. Bottom grilles around the perimeter of the island will absorb the impact of the iceberg, preventing direct contact with the pontoons. If the plastic pontoon island is anchored, and the iceberg is moving with the current or driven by the wind, its speed is low. There will be a smooth sliding sides, perhaps a partial twisting, but to cause the destruction of the pontoon structure before sinking, the iceberg cannot. In the process of operation, technical devices will be created that can eliminate possible collisions.
Plastic pontoon structures can be used on any water surfaces of oceans, lakes, rivers and even swamps, like Gati. The study of the topography of the ocean floor, flora and fauna, marine currents, Geology, climate will become more accessible.

|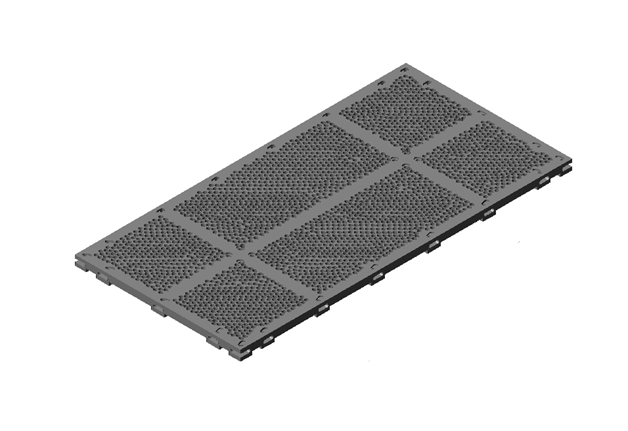 
|
Figure 3. Pontoon and bottom grille.
Body plastic pontoon has a through vertical hole and a center cross hole in a tube going horizontally. The holes are used for cable and side connections with each other and with bottom grids, as well as for the installation of various structures and devices (figure 3). Ventilation holes are provided for air circulation and moisture extraction from the inner chambers of the pontoon. The vents can block the access of air into the chambers of the pontoon, or on the contrary, to contain the gas or vacuum inside the chambers. In plastic pontoon structures, centralized, regulated ventilation in pontoon chambers can be used, due to the General ventilation system connecting the pontoons (Patent 2659315).
Plastic pontoon designs bottom grid attached to the pontoons at an angle of 15-30 degrees, go into the water, creating a "coast" zone. The design of the bottom gratings provides hydraulic control of the directions of motion of the wave flows. It compensates the lifting force of the bottom gratings (as the wing of the aircraft) and diverting the hydraulic shock waves from the bodies of pontoons. This group connection in a planar or three-dimensional design, provides a transition between air and water environments.
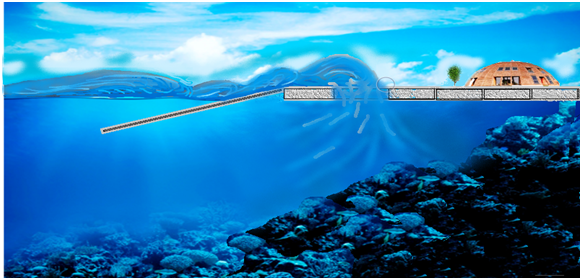
Figure 4. The scheme of movement of the wave on the bottom bars in the pool, through the pontoon.
The interaction of pontoons and bottom gratings in nature resemble a seashore when the wave coasting goes to the shoreline, reaches the splash line and flows back into the sea. On the bottom bars the wave slides and rises, reaching the first line of the pontoon row, behind which there is a series of pools. Rolling into the pool, it loses its destructive energy (figure 4). Thus, the plastic pontoon structure can withstand large waves (storm), away from the hydraulic shock waves, by flooding the pontoons under the wave, and the internal array of pontoons remains stationary.
In the case of a tsunami, when the water is approaching a wall of great height, a huge wave (for example, as a water Lily on the shore or algae) drowns, pressing to the bottom, shimmers, and the pontoons just float after the passage of the wave. People, at the time of passage of the wave over the pontoon system, need to hide in areas where there is a supply of air.
With the help of nanotechnology water filters have been invented. They allow you to obtain fresh water from ocean water by absorption. People and vegetation will be provided with fresh water on plastic pontoon structures. As a result of operation and with the use of nanotechnology, plastic bottom structures, over time, will be significantly improved and refined.
Initially, for the manufacture of pontoons and bottom gratings, the material is considered polyethylene terephthalate – thermoplastic, the most common representative of the class of polyesters, the product of polycondensation of ethylene glycol with terephthalic acid; solid, colorless transparent substance in the amorphous state and white, opaque in the crystalline state; durable, wear-resistant, good dielectric (Wikipedia). This polymer was developed in the Lab of macromolecular compounds of the Academy of Sciences in honor of what was called Dacron or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). From mid-1960-ies industrial PET were obtained by transesterification of dimethyl terephthalate with ethylene glycol with obtaining duplicaterecord, and subsequent polycondensation of the latter. In 1965, Amoco Corporation was able to improve the technology, resulting in widespread one-step synthesis of PET, ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid in a continuous pattern. It is noteworthy that the waste of polyethylene terephthalate after the mechanical and physico-chemical method is used for further injection molding and the physico-chemical properties of the polymer do not change. Features of the chemical structure of PET or PET is characterized by a combination of aliphatic, aromatic and carbonyl fragments opening the possibility of modifying the polymer and obtain materials with improved hydrophilic-hydrophobic and adhesive properties (Makarov, 2010).
Let us consider three carbon-containing chemicals-polyethylene terephthalate, graphite and diamond. Materials having the same chemical composition, but different structure are called polymorphic varieties, and the ability of the same chemical compounds to form crystals with different internal structure – polymorphism. Graphite and diamond are polymorphic forms of carbon. In the diamond structure, carbon atoms are bound by strong covalent bonds and form a three-dimensional framework. Therefore, diamond is the hardest mineral in nature. In the graphite structure, carbon atoms form planar structures with strong covalent bonds. However, individual flat layers of carbon atoms are bound between weak van der Waals bonds. Because of this, graphite is a very soft mineral. They differ in density: polyethylene terephthalate has a density of 1.455 g/cm3, graphite - 2.23 g/cm3, diamond - 3.55 g / cm3. The logical conclusion is that depending on the density of carbon-containing substances, their strength increases.
To increase the durability and strength of pontoons made of polyethylene terephthalate, cast product, it is necessary immediately after the crystallization of the plastic pontoon to act with high pressure. Create pressure in statistical presses (diamond anvils) or dynamically, when high pressure occurs for a short time of passage through the body of the pontoon strong shock wave. Due to its unique characteristics, carbon fiber plastics have found their application in modern industry, which can be used in the manufacture of pontoons. An active search for alternative materials based on graphene, metal micro - and nano - grids is underway. The unique results of the mechanism of formation of polymer composite materials based on polytetrafluoroethylene with carbon fibers (Vasiliev, 2017), organosilicon compounds are being developed and obtained.
Lomonosov M. V. believed that "no one should rush to ridicule hypotheses, because they are the only thing with which the greatest minds of the world were able to make discoveries". It is hoped that the hypothesis of the creation of new pontoons using shock waves, the use of new nanotechnology will allow:
- to place in the open ocean nano-plastic pontoon systems that can carry the construction of the dome type and other structures;
- grow fruit and berry crops;
- to provide people with their complete safety in the open ocean;
- arrange competitions on aircraft over pontoon airfields and diving under water.
The study identified the following shortcomings. Can a person live on the pontoon Islands without clogging the environment? How to clean the bottoms of the pontoons from the shell? How to protect plastic pontoon structures from spring ice drift on rivers? There are a lot of questions to be answered. Nature must be loved, understood and protected. Nature is our best assistant and a source of vital energy. The main thing is to get along with nature and not pass by its tips.
 2022-01-07
2022-01-07 241
241








